Slope of a Line
Definition of Slope
The slope of a line measures its steepness and rate of change. Given two points \(A(x_A,y_A)\) and \(B(x_B,y_B)\), the slope \(m\) is defined as:
\[ m = \frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x} = \frac{y_B - y_A}{x_B - x_A} \]
Where \(\Delta y = y_B - y_A\) is the vertical change (rise) and \(\Delta x = x_B - x_A\) is the horizontal change (run).

Special Cases
Horizontal Lines
For horizontal lines, \(y_A = y_B\), so:
\[ m = \frac{0}{x_B - x_A} = 0 \]
The equation of a horizontal line is \(y = \text{constant}\).
Vertical Lines
For vertical lines, \(x_A = x_B\), so:
\[ m = \frac{y_B - y_A}{0} = \text{undefined} \]
The equation of a vertical line is \(x = \text{constant}\).
Example Problems
Example 1: Finding Slopes
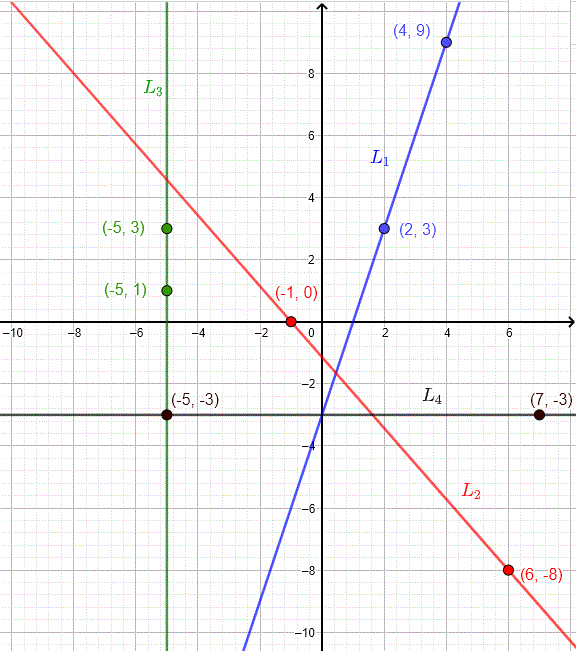
Determine slopes of lines through given points:
- \(L_1: (2,3), (4,9) \quad m_1 = \frac{9-3}{4-2} = 3\) (rises)
- \(L_2: (-1,0), (6,-8) \quad m_2 = \frac{-8-0}{6-(-1)} = -\frac{8}{7}\) (falls)
- \(L_3: (-5,1), (-5,3) \quad m_3 = \frac{3-1}{-5-(-5)} = \text{undefined}\) (vertical)
- \(L_4: (7,-3), (-5,-3) \quad m_4 = \frac{-3-(-3)}{-5-7} = 0\) (horizontal)
Example 2: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
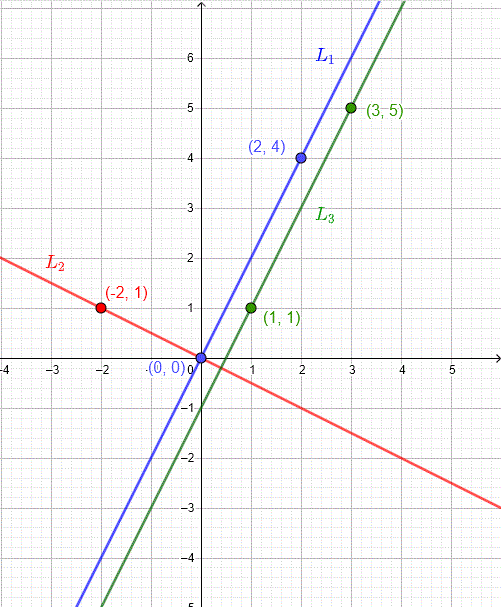
Given lines:
- \(L_1: (0,0), (2,4) \quad m_1 = 2\)
- \(L_2: (0,0), (-2,1) \quad m_2 = -\frac{1}{2}\)
- \(L_3: (1,1), (3,5) \quad m_3 = 2\)
Since \(m_1 = m_3\), \(L_1\) and \(L_3\) are parallel. Since \(m_1 \times m_2 = -1\), \(L_1\) and \(L_2\) are perpendicular.
Interactive Slope Explorer
How to Use the Interactive Graph:
- Drag points A and B to change the line's slope
- Watch the slope calculation update in real-time
- See the rise/run triangle and line equation
- Or enter coordinates below and click "Update from Coordinates"
Coordinate Input (Alternative to Dragging)
Tip: Drag the blue points on the graph for interactive control!
Slope Calculation
Formula: \(m = \dfrac{y_B - y_A}{x_B - x_A} = \dfrac{\text{Rise}}{\text{Run}}\)
Slope (m): 0.833 = 5/6
Equation of line: y = 5/6x - 1.333
\[y = \frac{5}{6}x - 1.333\]
Exploration Activities
- Drag point A or B to create different slopes
- Make a horizontal line by dragging points to have the same y-coordinate (\(y_A = y_B\))
- Make a vertical line by dragging points to have the same x-coordinate (\(x_A = x_B\))
- Create positive slopes (line rises left to right)
- Create negative slopes (line falls left to right)
- Observe how the rise/run triangle changes
- Note that slope = rise/run = (\(y_B - y_A\))/(\(x_B - x_A\))
Related Resources


