Calculate Areas of Squares, Rectangles, Triangles,
Parallelograms and Trapezoids - Grade 6
Grade 6 examples and questions to calculate areas of rectangles, squares, triangles, parallelograms and trapezoids with detailed solutions and explanations are presented.
Formulas to Calculate Areas
The formulas to calculate the areas of rectangles, squares, triangles, parallelograms and trapezoids are presented.
|
 . .
Rectangle: Area = L × W
|
 . .
Square: Area = S × S = S 2
|
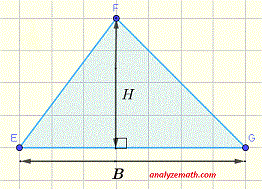 . .
Triangle: Area = (1 / 2) × H × B
|
|
 . .
Parallelogram: Area = L × H
|
 . .
Trapezoid: Area = (1 / 2) × H × (B1 + B2)
|
|
Answer the Following Questions
-
Use the grid to determine the dimensions of the figures below and then use the formulas to calculate their areas.
 .
.
Determine the dimensions of the figures below and then calculate their areas.
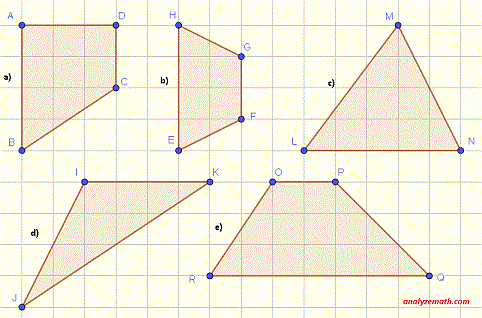 .
.
Solutions to the Above Problems
-
Solution
We first determne the dimensions needed to calculate the area then use the formulas for each figure.
- The figure in part a) is a rectangle of width AD = 3 units and length DC = 4 units. Hence the area is given by
Area = Length × witdh = 4 × 3 = 12 unit 2
- The figure in part b) is a square of side HG = 3 units. Hence the area is given by
Area = Side × Side = 3 × 3 = 9 unit 2
- The figure in part c) is a right triangle of height H = ML = 3 and base B = MN = 4. The area is given by
Area = (1 / 2) × H × B = (1 / 2) × 3 × 4 = 6 unit 2
- The figure in part d) is a right triangle of same dimension as the right triangle in part c): Height H = IJ = 3 and base B = JK = 4. The area is given by
Area = (1 / 2) × H × B = (1 / 2) × 3 × 4 = 6 unit 2
- The figure in part e) is a parallelogram of length L = OP = 5 units and the distance H between OP and RQ = 3 units (see figure below) . The area is given by
 .
.
Area = L × H = 5 × 3 = 15 unit 2
Note that H is perpendicular to both OP and RQ.
-
Solution
We first need to identify the figure, determine its dimensions and then calcualte the area.
- The figure in part a) is a trapezoid with AB and DC parallel. Base B1 = DC = 2 units, base B2 = AB = 4 and the height H = AD = 3 units. Hence the area is given by
Area = (1 / 2) × H × (B1 + B2) = ( 1 / 2) × 3 × (2 + 4) = ( 1 / 2) × 3 × 6 = (1 / 2) × 18 = 18 / 2 = 9 unit 2
- The figure in part b) is a trapezoid with GF and HE parallel. Base B1 = GF = 2 units, base B2 = HE = 4 and the height H = 2 units. Hence the area is given by
Area = (1 / 2) × H × (B1 + B2) = ( 1 / 2) × 2 × (2 + 4) = ( 1 / 2) × 2 × 6 = (1 / 2) × 12 = 12 / 2 = 6 unit 2
- The figure in part c) is a triangle of base B = LN = 5 units and height H = 4 units (see figure below). The area is given by
 .
.
Area = (1 / 2) × B × H = (1 / 2) × 5 × 4 = (1 / 2) × 20 = 20 / 2 = 10 unit 2
- The figure in part d) is a triangle of base B = IK = 4 units and height H = 4 units (see figure below). The area is given by
 .
.
Area = (1 / 2) × B × H = (1 / 2) × 4 × 4 = (1 / 2) × 16 = 16 / 2 = 8 unit 2
- The figure in part e) is a trapezoid with base B1 = OP = 2 units, base B2 = RQ = 7 units and height H = 3. . The area is given by
Area = (1 / 2) × H × (B1 + B2) = ( 1 / 2) × 3 × (2 + 7) = ( 1 / 2) × 2 × 9 = (1 / 2) × 27 = 27 / 2 = 13.5 unit 2
 .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
.