Question
\(4 \times 10^{-5} =\)
Solution
Rewrite \(4 \times 10^{-5}\) as
\[ \frac{4}{10^{5}} = \frac{4}{100,\!000} = 0.00004 \]Question
Which of the following is equivalent to \((x)(x)(x)(x^{3})\), for all \(x\)?
Solution
Rewrite \((x)(x)(x)(x^{3})\) as
\[ (x)(x)(x)(x^{3}) = (x)^{3} (x^{3}) = x^{6} \]Question
There are 15 balls in a box: 8 balls are green, 4 are blue and 3 are white. Then 1 green and 1 blue balls are taken from the box and put away. What is the probability that a blue ball is selected at random from the box?
Solution
If 1 green and 1 blue ball are taken from the box, then there are 7 green, 3 blue and 3 white balls, a total of 13 balls. If one ball is selected at random, the probability that it is blue is given by
\[ \frac{3}{13} \]Question
The length of a rectangle is 3 times its width. If the width of the rectangle is 5 inches, what is the rectangle's area, in square inches?
Solution
If the width is 5 in and the length is 3 times the width, then the length is
\[ 3 \times 5 = 15 \text{ in} \]The area is given by
\[ 5 \times 15 = 75 \text{ in}^2 \]Question
For all \(x > 2\), \(\frac{2x^{2} + 2x - 12}{x - 2}\) simplifies to
Solution
We first factor \(2x^{2} + 2x - 12\) as follows
\[ 2x^{2} + 2x - 12 = 2(x^{2} + x - 6) = 2(x + 3)(x - 2) \]We simplify as follows
\[ \frac{2x^{2} + 2x - 12}{x - 2} = \frac{2(x + 3)(x - 2)}{x - 2} = 2(x + 3) \]Question
If the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 10 inches long and one of its legs is 5 inches long, how long is the other leg?
Solution
Let \(x\) be the length of second leg and apply Pythagoras' theorem as follows
\[ 10^{2} = 5^{2} + x^{2} \]Solve for \(x\)
\[ x = \sqrt{100 - 25} = \sqrt{75} = 5\sqrt{3} \]Question
In the standard \((x,y)\) coordinate plane, the graph of \((x + 3)^{2} + (y + 5)^{2} = 16\) is a circle. What is the circumference of the circle, expressed in coordinate units?
Solution
Rewrite the given equation as follows
\[ (x + 3)^{2} + (y + 5)^{2} = 4^{2} \]The radius of the circle is 4 and therefore the circumference is given by
\[ 2 \times 4 \times \pi = 8\pi \]Question
How many solutions are there to the equation \(x^{2} - 7 = 0\)?
Solution
Rewrite the given equation as follows
\[ x^{2} = 7 \]The above equation has two solutions \(+\sqrt{7}\) and \(-\sqrt{7}\).
Question
A circle with center \((4,-5)\) is tangent to the y-axis in the standard \((x,y)\) coordinate plane. What is the radius of this circle?
Solution
The radius is given by the distance between the center of the circle \((4, -5)\) and the y-axis which is 4.
Question
Angle \(A\) is an acute angle and \(\sin(A) = \frac{11}{14}\). What is the value of \(\cos(A)\)?
Solution
\(\sin(A)\) and \(\cos(A)\) are related by
\[ \sin^{2}(A) + \cos^{2}(A) = 1 \]Substitute \(\sin(A)\) by \(\frac{11}{14}\) in the above equation
\[ \left(\frac{11}{14}\right)^{2} + \cos^{2}(A) = 1 \]Solve for \(\cos(A)\) and select the positive value since \(A\) is an acute angle
\[ \cos(A) = \sqrt{1 - \frac{121}{196}} = \sqrt{\frac{196 - 121}{196}} = \frac{\sqrt{75}}{14} = \frac{5\sqrt{3}}{14} \]Question
What are the values of \(a\) and \(b\), if any, where \(-a|b + 4| > 0\)?
Solution
For \(-a |b + 4| > 0\), \(-a\) must be positive and \(|b + 4|\) must also be positive. Which means \(a\) must be negative and \(b + 4 \neq 0\) or \(b \neq -4\).
\(a < 0\) and \(b \neq -4\).
Question
In a shipment of televisions, \(1/50\) of the televisions are defective. What is the ratio of defective to nondefective televisions?
Solution
If \(1/50\) are defective, then
\[ 1 - \frac{1}{50} = \frac{49}{50} \text{ are not defective} \]So if \(x\) is the total number of TV sets, then \(\frac{1}{50}x\) are defective and \(\frac{49}{50}x\) are not defective. Hence the ratio of defective to nondefective is given by
\[ \frac{x(1/50)}{x(49/50)} = \frac{1}{50} \cdot \frac{50}{49} = \frac{1}{49} \]Question
Which of the following is divisible (with no remainder) by 4?
Solution
A whole number is divisible by 4 if the number formed by the last two digits is divisible by 4. The numbers formed by the last two digits of the given numbers are: 33, 56, 69, 17 and 95. The only one that is divisible by 4 is 56 and therefore 510056 is the only number in the list that is divisible by 4.
Question
A particle travels \(1 \times 10^{6}\) meters per second in a straight line for \(5 \times 10^{-6}\) seconds. How many meters has it traveled?
Solution
We are given the speed \(1 \times 10^{6}\) m/s and the time \(5 \times 10^{-6}\) seconds. The distance \(d\) is given by
\[ d = (1 \times 10^{6} \text{ m/s}) \times (5 \times 10^{-6} \text{ s}) = 5 \times 10^{6 + (-6)} = 5 \times 10^{0} = 5 \text{ meters} \]Question
The lengths of sides AB and AC in the triangle below are equal. What is the measure of angle \(A\)?

Solution
Since the lengths of sides AB and AC are equal, then the triangle is isosceles and therefore angles B and C are equal in size. Hence angle \(A\) is given by
\[ 180^{\circ} - (70^{\circ} + 70^{\circ}) = 40^{\circ} \]Question
In the figure below ABC is an equilateral triangle. AH is perpendicular to BC and has a length of \(2\sqrt{3}\) inches. What is the area, in square inches, of triangle \(ABC\)?
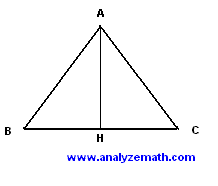
Solution
Let \(x\) be the length of the side of the equilateral triangle. Since \(AH\) is perpendicular to \(BC\), then by Pythagoras' theorem (applied to triangle ABH) we can write
\[ x^{2} = \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)^{2} + (2\sqrt{3})^{2} \]Simplify the above equation
\[ x^{2} = \frac{x^{2}}{4} + 12 \] \[ 4x^{2} = x^{2} + 48 \] \[ 3x^{2} = 48 \] \[ x^{2} = 16 \]Solve to find \(x = 4\)
The area \(A\) of the triangle is given by
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times AH \times BC = \frac{1}{2} \times 2\sqrt{3} \times 4 = 4\sqrt{3} \]Question
If \(8y = 3x - 11\), then \(x =\)
Solution
We are asked to solve for \(x\). Add 11 to both sides of the equation and simplify
\[ 8y + 11 = 3x - 11 + 11 \] \[ 8y + 11 = 3x \]Divide both sides of the equation by 3
\[ x = \frac{8y + 11}{3} \]Question
Which of the statements describes the solution set for \(-2(x + 8) = -2x + 20\)?
A) \(x = -2\) only
B) \(x = 0\) only
C) \(x = 20\) only
D) There are no solutions for this equation.
E) All real numbers are solutions of this equation.
Solution
Expand the left side of the equation
\[ -2x - 16 = -2x + 20 \]Add \(2x\) to both sides
\[ -2x - 16 + 2x = -2x + 20 + 2x \] \[ -16 = 20 \]The last statement is always false, hence the given equation has no solution.
Question
When graphed in the \((x,y)\) coordinate plane, at what point do the lines \(2x + 3y = 5\) and \(x = -2\) intersect?
Solution
We need to solve the system of equations:
\[ \begin{cases} 2x + 3y = 5 \\ x = -2 \end{cases} \]Substitute \(x = -2\) into the first equation:
\[ 2(-2) + 3y = 5 \] \[ -4 + 3y = 5 \] \[ 3y = 9 \] \[ y = 3 \]The lines intersect at \((-2, 3)\).
Question
The area of a trapezoid is \(0.5h(b_1 + b_2)\), where \(h\) is the altitude, and \(b_1\) and \(b_2\) are the lengths of the parallel bases. If a trapezoid has an altitude of 15 inches, an area of 105 square inches, and one of the bases 22 inches, what is the perimeter, in inches, of the trapezoid?
Solution
Given the area, \(h\) and \(b_1\), we find \(b_2\):
\[ 105 = 0.5 \times 15 \times (22 + b_2) \] \[ 105 = 7.5 \times (22 + b_2) \] \[ b_2 = \frac{105}{7.5} - 22 = 14 - 22 = -8 \]The base of a trapezoid cannot be negative. Therefore, no trapezoid exists with the given dimensions.
Question
If you drove at an average speed of 66 miles per hour, what distance, in miles, did you drive in 99 minutes?
Solution
First convert the speed to miles per minute:
\[ \frac{66}{60} = 1.1 \text{ miles per minute} \]The distance is:
\[ 1.1 \times 99 = 108.9 \text{ miles} \]Question
If \(x\) and \(y\) are any real numbers such that \(0 < x < 2 < y\), which of these must be true?
A) \(x < \frac{xy}{2} < y\)
B) \(0 < xy < 2x\)
C) \(x < xy < 2\)
D) \(0 < xy < 2\)
E) \(xy < y\)
Solution
Since both \(x\) and \(y\) are positive, the inequality \(x < 2 < y\) implies
\[ \frac{1}{x} > \frac{1}{2} > \frac{1}{y} \]Multiply all terms by \(xy\) (positive) and simplify:
\[ y > \frac{xy}{2} > x \]Which is equivalent to
\[ x < \frac{xy}{2} < y \]This corresponds to option A. Using \(x=1.8\) and \(y=2.1\), it can be shown that B, C, D, and E are not necessarily true.
Question
In the right triangle ABC below, what is the cosine of angle \(A\)?

Solution
First find the hypotenuse \(BA\):
\[ BA = \sqrt{3^{2} + 4^{2}} = 5 \]Then
\[ \cos(A) = \frac{\text{adjacent}}{\text{hypotenuse}} = \frac{3}{5} \]Question
The graph of \(y = \frac{2}{x - 3}\) is shown below. Among the following, which is the best possible graphical representation of \(y = -\frac{2}{|x - 3|}\)?


Solution
\(|x - 3|\) is always positive or zero. Hence \(-\frac{2}{|x - 3|}\) is always negative except at \(x = 3\) where it is undefined. The graph in C is entirely below the x-axis and is therefore the closest to the graph of \(y = -\frac{2}{|x - 3|}\).
Question
What is the slope of the line \(4x = -3y + 8\)?
Solution
Write the equation in slope-intercept form \(y = mx + b\):
\[ 4x = -3y + 8 \] \[ 3y = -4x + 8 \] \[ y = -\frac{4}{3}x + \frac{8}{3} \]The slope is \(-\frac{4}{3}\).
Question
In the figure below, B is on \(\overline{AD}\), \(\angle BAC\) and \(\angle ACB\) measure \(26^{\circ}\) and \(131^{\circ}\) respectively. What is the measure of \(\angle CBD\)?
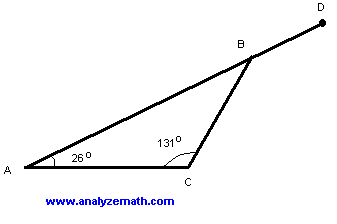
Solution
First find \(\angle ABC\) using the sum of angles in triangle ABC:
\[ \angle ABC = 180^{\circ} - (26^{\circ} + 131^{\circ}) = 23^{\circ} \]Angles ABC and CBD are supplementary:
\[ \angle CBD = 180^{\circ} - 23^{\circ} = 157^{\circ} \]Question
Which of the following is equal to \(\sqrt{45}\)?
Solution
\[ \sqrt{45} = \sqrt{9 \times 5} = \sqrt{9} \cdot \sqrt{5} = 3\sqrt{5} \]Question
What is the smallest value of \(x\) that satisfies the equation \(x(x + 4) = -3\)?
Solution
Rewrite the equation:
\[ x^{2} + 4x + 3 = 0 \]Factor:
\[ (x + 3)(x + 1) = 0 \]Solutions: \(x = -3\) and \(x = -1\). The smallest is \(-3\).
Question
A group of 7 friends are having lunch together. Each person eats at least \(\frac{3}{4}\) of a pizza. What is the smallest number of whole pizzas needed for lunch?
Solution
The total amount of pizza needed is at least:
\[ 7 \times \frac{3}{4} = \frac{21}{4} = 5.25 \]Therefore, at least 6 whole pizzas are needed.
Question
All axes in the graphs below have the same scales. Which one of the graphs is closest to the graph of \(y = -2x + 2\)?

Solution
Find the intercepts:
x-intercept: set \(y=0\):
\[ 0 = -2x + 2 \Rightarrow x = 1 \quad (1,0) \]y-intercept: set \(x=0\):
\[ y = 2 \quad (0,2) \]Using these intercepts, the closest graph is D.
Question
The measures of angles A, B and C of a triangle are in the ratio 3:4:5. What is the measure, in degrees, of the largest angle?
Solution
Let the angles be \(3x\), \(4x\), and \(5x\). Their sum is \(180^{\circ}\):
\[ 3x + 4x + 5x = 180^{\circ} \] \[ 12x = 180^{\circ} \] \[ x = 15^{\circ} \]The largest angle is \(5x = 5 \times 15^{\circ} = 75^{\circ}\).
Question
There are \(n\) students in a school. If \(r\%\) among the students are 12 years or younger, which of the following expressions represents the number of students who are older than 12?
Solution
If \(r\%\) are 12 or younger, then \((100 - r)\%\) are older than 12. The number of students older than 12 is:
\[ n \times \frac{100 - r}{100} \]Question
If \(x + 4y = 5\) and \(5x + 6y = 7\), then \(3x + 5y = ?\)
Solution
Add the two equations:
\[ (x + 4y) + (5x + 6y) = 5 + 7 \] \[ 6x + 10y = 12 \]Divide by 2:
\[ 3x + 5y = 6 \]Question
Which integer is nearest to \(\frac{\sqrt{2100}}{\sqrt{7}}\)?
Solution
\[ \frac{\sqrt{2100}}{\sqrt{7}} = \sqrt{\frac{2100}{7}} = \sqrt{300} \approx 17.32 \]The nearest integer is 17.
Question
For all real numbers \(x\), the minimum value of \(1 + 2\cos(4x)\) is
Solution
The range of \(\cos(4x)\) is \([-1, 1]\). Therefore,
\[ -2 \leq 2\cos(4x) \leq 2 \]Add 1:
\[ -1 \leq 1 + 2\cos(4x) \leq 3 \]The minimum value is \(-1\).
Question
What is the largest possible product for 2 odd integers whose sum is equal to 32?
Solution
Let the odd integers be \(2n+1\) and \(2k+1\). Their sum is 32:
\[ (2n+1) + (2k+1) = 32 \] \[ 2n + 2k = 30 \] \[ n + k = 15 \]The product \(P\) is:
\[ P = (2n+1)(2k+1) = 4nk + 2n + 2k + 1 = 4nk + 2(n+k) + 1 = 4nk + 31 \]To maximize \(P\), maximize \(nk\) given \(n+k=15\). The maximum occurs when \(n\) and \(k\) are as close as possible. Since \(n\) and \(k\) are integers, the maximum product is when the numbers are 15 and 17 or 17 and 15. The product is \(15 \times 17 = 255\).
Question
If \((a + b)^{2} = 25\) and \((a - b)^{2} = 45\), then \(a^{2} + b^{2} = ?\)
Solution
Expand both equations:
\[ a^{2} + 2ab + b^{2} = 25 \] \[ a^{2} - 2ab + b^{2} = 45 \]Add them:
\[ 2a^{2} + 2b^{2} = 70 \] \[ a^{2} + b^{2} = 35 \]Question
If \(a = 3\), then \(\frac{2}{\frac{1}{7} + \frac{1}{a}} = ?\)
Solution
\[ \frac{2}{\frac{1}{7} + \frac{1}{3}} = \frac{2}{\frac{3+7}{21}} = \frac{2}{\frac{10}{21}} = 2 \times \frac{21}{10} = \frac{42}{10} = \frac{21}{5} \]Question
A company makes a profit equal to 25% of its sales. The profit is shared equally among the 4 owners of the company. If the company generates sales of $5,000,000, how much money does each one of the owners get?
Solution
Profit = \(25\% \times 5,000,000 = 1,250,000\).
Each owner gets \(\frac{1,250,000}{4} = 312,500\).
Question
If the expression \(x^{3} + 2hx - 2\) is equal to 6 when \(x = -2\), what is the value of \(h\)?
Solution
Substitute \(x = -2\):
\[ (-2)^{3} + 2h(-2) - 2 = 6 \] \[ -8 - 4h - 2 = 6 \] \[ -4h = 16 \] \[ h = -4 \]Question
If \(-\frac{3}{a - 3} = \frac{3}{a + 2}\), then \(a = ?\)
Solution
Cross multiply:
\[ -3(a + 2) = 3(a - 3) \] \[ -3a - 6 = 3a - 9 \] \[ -6a = -3 \] \[ a = \frac{1}{2} \]Question
For what negative value of \(k\), the system of equations below has no solutions?
\[ \begin{cases} 2x + ky = 5 \\ kx + (k+4)y = 7 \end{cases} \]Solution
The system has no solution if the determinant of the coefficient matrix is zero and the equations are inconsistent. The determinant is:
\[ \begin{vmatrix} 2 & k \\ k & k+4 \end{vmatrix} = 2(k+4) - k^{2} = -k^{2} + 2k + 8 \]Set to zero:
\[ -k^{2} + 2k + 8 = 0 \] \[ k^{2} - 2k - 8 = 0 \] \[ (k-4)(k+2) = 0 \]The negative value is \(k = -2\).
Question
The two legs of a right triangle measure 6 and 8 inches respectively. What is the area of the circle that contains all 3 vertices of the triangle?
Solution
The hypotenuse is the diameter of the circle. Find hypotenuse:
\[ d = \sqrt{6^{2} + 8^{2}} = 10 \]Radius \(r = 5\). Area of circle:
\[ \pi r^{2} = 25\pi \]Question
\(X\) and \(Y\) are acute angles such that \(\tan Y = \cot X\). What is the sum, in degrees, of the measures of the angles \(X\) and \(Y\)?
Solution
\(\tan Y = \cot X\) implies \(\tan Y = \frac{1}{\tan X}\), so \(\tan X \tan Y = 1\).
Using the identity:
\[ \tan(X+Y) = \frac{\tan X + \tan Y}{1 - \tan X \tan Y} \]Since \(\tan X \tan Y = 1\), the denominator is zero, so \(\tan(X+Y)\) is undefined, meaning \(X+Y = 90^{\circ}\).
Question
The measures of the sides of the right triangle below are in inches. What is the value of \(x\)?

Solution
Using tangent:
\[ \tan(60^{\circ}) = \frac{1}{x} \] \[ x = \frac{1}{\tan(60^{\circ})} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \]Question
Which of the graphs below is the solution set of \(-3x \le 12\)?

Solution
Divide both sides by \(-3\) (reverse inequality):
\[ x \ge -4 \]This corresponds to graph C.
Question
Which of the lines below is not parallel to the line \(6x - 2y = 10\)?
A) \(3x - y = 7\)
B) \(-6x + 2y = 20\)
C) \(3x + y = 7\)
D) \(6x - 2y = 5\)
E) \(x - \frac{y}{3} = 9\)
Solution
The slope of the given line is found by rewriting:
\[ 6x - 2y = 10 \Rightarrow y = 3x - 5 \Rightarrow \text{slope} = 3 \]Check each option:
A) \(y = 3x - 7\), slope 3.
B) \(y = 3x + 10\), slope 3.
C) \(y = -3x + 7\), slope -3 → not parallel.
D) \(y = 3x - \frac{5}{2}\), slope 3.
E) \(y = 3x - 27\), slope 3.
Answer is C.
Question
For what value of \(k\) the equation below has no solution?
\[ 2x + 3 = x - 2kx - 5 \]Solution
Simplify:
\[ 2x + 3 = x(1 - 2k) - 5 \] \[ 2x - x(1 - 2k) = -5 - 3 \] \[ x(2 - (1 - 2k)) = -8 \] \[ x(1 + 2k) = -8 \]If \(1 + 2k = 0\), then \(k = -\frac{1}{2}\), and the equation becomes \(0 = -8\), which has no solution.
Question
\(|5 - 2| - |6 - 9| = ?\)
Solution
\[ |3| - |-3| = 3 - 3 = 0 \]Question
What is the average of \(\frac{7}{8}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\)?
Solution
\[ \frac{\frac{7}{8} + \frac{3}{4}}{2} = \frac{\frac{7}{8} + \frac{6}{8}}{2} = \frac{\frac{13}{8}}{2} = \frac{13}{16} \]Question
A solution is made of water and pure acid. If 75% of the solution is water, how many liters of pure acid are in 20 liters of this solution?
Solution
If 75% is water, then 25% is acid. The amount of acid is:
\[ 25\% \times 20 = 0.25 \times 20 = 5 \text{ liters} \]Question
The total surface area of all six faces of the rectangular box below is equal to 128 square inches. What is \(x\) in inches?

Solution
The surface area is:
\[ 2(4x) + 2(4x) + 2(4 \times 4) = 128 \] \[ 8x + 8x + 32 = 128 \] \[ 16x = 96 \] \[ x = 6 \]Question
The diagonal of a square has a measure of 12 inches. What is the perimeter, in inches, of this square?
Solution
Let side be \(s\). By Pythagoras:
\[ s^{2} + s^{2} = 12^{2} \] \[ 2s^{2} = 144 \] \[ s^{2} = 72 \] \[ s = 6\sqrt{2} \]Perimeter = \(4s = 24\sqrt{2}\).
Question
The lengths in the rectangle below are in inches. What is the shaded area in square inches?

Solution
Total area of rectangle = \(7 \times (6+4) = 70\).
Non-shaded area = sum of areas of three triangles:
\[ \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 7 + \frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 4 + \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 2 = 21 + 8 + 3 = 32 \]Shaded area = \(70 - 32 = 38\).
Question
In the right triangle ABC, C is a right angle and the measure of angle B is \(60^{\circ}\). If \(\overline{BC}\) is 20 inches long, then how long is \(\overline{AC}\)?

Solution
Using tangent:
\[ \tan(60^{\circ}) = \frac{AC}{BC} \] \[ AC = BC \times \tan(60^{\circ}) = 20 \times \sqrt{3} \]Question
In the figure below ABC is a right triangle. ABDE is a square of area 200 square inches and BCGF is a square of 100 square inches. What is the length, in inches, of \(\overline{AC}\)?

Solution
Side of square ABDE = \(\sqrt{200} = 10\sqrt{2}\).
Side of square BCGF = \(\sqrt{100} = 10\).
Using Pythagoras in triangle ABC:
\[ AC^{2} = (10\sqrt{2})^{2} + 10^{2} = 200 + 100 = 300 \] \[ AC = \sqrt{300} = 10\sqrt{3} \]Question
If \(x = 2.0001\), which of the following expressions has the largest value?
A) \(\frac{2}{x+2}\)
B) \(\frac{2}{x-2}\)
C) \(\frac{x+2}{2}\)
D) \(\frac{2}{x}\)
E) \(\frac{x}{2}\)
Solution
For \(x=2.0001\), the denominator in B is very small (\(0.0001\)), making the fraction very large. So B has the largest value.
Question
In the rectangle below, the measure of the length \(\overline{AD}\) is 3 times the measure of the width \(\overline{AB}\). What is the slope of the line segment \(\overline{BD}\)?

Solution
Let \(AB = w\), then \(AD = 3w\). Coordinates: \(B(0,w)\), \(D(3w, 0)\). Slope of BD:
\[ \frac{0 - w}{3w - 0} = - \frac{1}{3} \]Question
What is the product of the two real solutions of the equation \(2x = 3 - x^{2}\)?
Solution
Rewrite:
\[ x^{2} + 2x - 3 = 0 \]Factor:
\[ (x+3)(x-1) = 0 \]Solutions: \(x=-3\) and \(x=1\). Product = \(-3 \times 1 = -3\).
Question
Which of the following equations corresponds the data in the table?
| x | y |
| -20 | -1/8 |
| -10 | -1/3 |
| 0 | 1/2 |
| 5 | 2/9 |
| 20 | 1/12 |
A) \(y = \frac{1}{x+2}\)
B) \(y = \frac{2}{x+4}\)
C) \(y = \frac{x-1}{x+2}\)
D) \(y = \frac{2}{x-2}\)
E) \(y = \frac{1}{2x+2}\)
Solution
Test each option with a point from the table, e.g., (0,1/2):
A: \(y = \frac{1}{0+2} = \frac{1}{2}\) → works.
B: \(y = \frac{2}{0+4} = \frac{1}{2}\) → works.
C: \(y = \frac{0-1}{0+2} = -\frac{1}{2}\) → fails.
D: \(y = \frac{2}{0-2} = -1\) → fails.
E: \(y = \frac{1}{0+2} = \frac{1}{2}\) → works.
Now test another point, e.g., (5,2/9):
A: \(y = \frac{1}{5+2} = \frac{1}{7}\) → fails.
B: \(y = \frac{2}{5+4} = \frac{2}{9}\) → works.
E: \(y = \frac{1}{10+2} = \frac{1}{12}\) → fails.
So the correct equation is B.