Sine Function sin x
Definition and Graph of the Sine Function
We first consider angle θ with initial side on the positive x axis (in standard position) and terminal side OM as shown below.

The sine function is defined as
\[ \sin(\theta) = \dfrac{y}{r} \]
where \( r \ \) is the distance from the origin O to any point M on the terminal side of the angle and is given by
\[ r = \sqrt{x^2+y^2} \]
If point M on the terminal side of angle θ is such that OM = r = 1, we may use a circle with radius equal to 1 called unit circle to evaluate the sine function as follows:
\[ sin(\theta) = y / r = y / 1 = y\]
\( \sin(\theta) \) is equal to the y coordinate of a point on the terminal side of an angle in standard position and also on a unit circle.
It is even easier and no calculator is needed to find \( \sin(\theta) \) for the quadrantal angles: \( 0, \dfrac{\pi}{2}, \pi, ... \) as shown in the unit circle below:
The coordinates of the point corresponding to \( \theta = 0 \) on the unit circle are: (1,0). The y coordinate is equal to 0, hence \( \sin(0) = 0\)
The coordinates of the point corresponding to \( \theta = \dfrac{\pi}{2} \) on the unit circle are: (0,1). The y coordinate is equal to 1, hence \( \sin(\dfrac{\pi}{2}) = 1\)
and so on.

Let us now put the values of the quadrantal angles angles \( 0, \dfrac{\pi}{2}, \pi, \dfrac{3\pi}{2} , 2\pi \) and the values of their sine on a table as shown below.
| \( \theta \) | \( \sin(\theta) \) |
| \( 0 \) | \( 0 \) |
| \( \dfrac{\pi}{2} \) | \( 1 \) |
| \( \pi \) | \( 0 \) |
| \( \dfrac{3\pi}{2} \) | \( -1 \) |
| \( 2\pi \) | \( 0 \) |
We now use a system of rectangular axes \( (x,y) \) to plot the points in the above table and approximate the graph of the sine function as shown below.
NOTE however that because we are used to \( x \) being the variable of a function, \(x\) on the graph takes values of \( \theta \) and y takes the values of \( \sin(\theta) \) which is noted as \( y = \sin(x) \).
After \( 2\pi \), and as \( \theta \) increases, the values of \( \sin(\theta) \) will repeat at the quadrantal angles. We say that the sine function has a period of \( 2\pi \) shown below in red.
.gif)
General Sine Functions
A more general sine function is written as
\( f(x) = a \sin(b x + c) + d \)
with its amplitude \( |a| \) , period \( \dfrac{2\pi}{|b|} \) and phase shift \( -\dfrac{c}{b} \) are explored interactively using an html 5 applet. The investigation is carried out by changing the parameters \( a, b, c\) and \( d \). To deeply understand the effects of each parameter on the graph of the function, we change one parameter at the time at the start. Then later we may change more than one parameter.
Exploration and understanding of the phase shift is done by comparing the shift between the graphs of the two functions:
\( f(x) = a \sin(b x + c) + d \)
in blue and
\( g(x) = a \sin(b x) + d \)
in red as shown in the figure below.
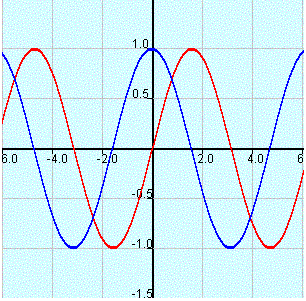
You may also want to consider another tutorial on the trigonometric unit circle .
Interactive Tutorial Using Html 5 applet
\( y = f(x) = a \sin(b x + c) + d \) , in blue (with phase shift)
\( y = f(x) = a \sin(b x) + d \) , in red (with no phase shift, c = 0)
How do the 4 coefficients a, b, c and d affect the graph of f(x)?
Amplitude
Set a = 1, b = 1, c = 0 and d = 0. Write down f(x) and take note of the amplitude, period and phase shift of f(x)? Now change a , how does it affect the graph? The amplitude is defined as \( |a| \).
Answer
Period
set a = 1, c = 0, d = 0 and change b. Find the period from the graph and compare it to \( \dfrac{2\pi}{|b|} \). How does b affect the perid of the graph of f(x)?
The period is the horizontal distance (along the x-axis) between two points: one is the starting point of a cycle and the second is the end point of the same cycle; two successive maxima or minima for example.
Answer
Phase Shift
set a = 1, b = 1, d = 0 and change parameter c starting from zero going slowly to positive larger values. Take note of the shift, is it left or right?
Answer
set a = 1, b = 1, d = 0 and change parameter c starting from zero going slowly to negative smaller values. Take note of the shift, is it left or right?
Answer
repeat the above for b = 2, 3 and 4, measure the shift and compare it to - c/b (the phase shift).
Answer
Vertical Shift
set a, b and c to non zero values and change d. What is the direction of the shift of the graph?
Answer
More References and Links on Sine Functions
Explore interactively the Derivatives of Sine (sin x) Functions
Match Sine Functions to Graphs. Excellent activity where graphs and functions are matched.
Explore interactively the sum of a sine and a cosine functionsSum of Sine and Cosine Functions
Examples with detailed solutions and explanations on sine function problems. Tutorial on Sine Functions (1)- Problems
Tutorial on the relationship between the amplitude, the vertical shift and the maximum and minimum of the sine functionTutorial on Sine Functions (2)- Problems
Trigonometric Functions
Step by step graphing of sine functionsGraph of Sine, a*sin(bx+c), Function
Explore interactively the relationship between the graph of sine function and the coordinates of a point on the unit circle Unit Circle and Trigonometric Functions sin(x), cos(x), tan(x)
The Six Trigonometric Functions Calculator.


.gif)
