Inscribed right triangle problem with detailed solution.
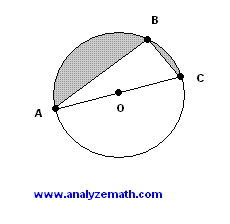
In the figure below, triangle \(ABC\) is inscribed inside the circle with center \(O\) and radius \(r = 10\) cm. Find the lengths of \(AB\) and \(CB\) so that the area of the shaded region is twice the area of the triangle.

Since \(O\) lies on \(AC\), \(AC\) is a diameter of the circle. By Thales's theorem, triangle \(ABC\) has a right angle at \(B\).
Let:

The combined area of the triangle and shaded region equals half the circle's area: \[ A_t + A_s = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi (10)^2 = 50\pi. \] Substituting \(A_s = 2A_t\): \[ A_t + 2A_t = 50\pi \quad \Rightarrow \quad 3A_t = 50\pi \quad \Rightarrow \quad A_t = \frac{50\pi}{3}. \]
Using angle \(A\) (internal to the triangle): \[ \sin A = \frac{CB}{AC} = \frac{CB}{20} \quad \Rightarrow \quad CB = 20 \sin A, \] \[ \cos A = \frac{AB}{AC} = \frac{AB}{20} \quad \Rightarrow \quad AB = 20 \cos A. \] The area \(A_t\) can also be expressed as: \[ A_t = \frac{1}{2} \cdot AB \cdot CB = \frac{1}{2} (20 \cos A)(20 \sin A) = 200 \cos A \sin A. \] Using the identity \(\sin 2A = 2 \sin A \cos A\): \[ A_t = 100 \sin 2A. \] Equating with the earlier expression: \[ 100 \sin 2A = \frac{50\pi}{3} \quad \Rightarrow \quad \sin 2A = \frac{\pi}{6} \approx 0.5236. \]
Solving for \(2A\): \[ 2A = \arcsin(0.5236) \approx 31.6^\circ \quad \text{or} \quad 2A = 180^\circ - 31.6^\circ = 148.4^\circ. \] Thus: \[ A \approx 15.8^\circ \quad \text{or} \quad A \approx 74.2^\circ. \]
First solution (\(A \approx 15.8^\circ\)): \[ AB = 20 \cos 15.8^\circ \approx 19.24 \text{ cm}, \quad CB = 20 \sin 15.8^\circ \approx 5.45 \text{ cm}. \] Second solution (\(A \approx 74.2^\circ\)): \[ AB = 20 \cos 74.2^\circ \approx 5.45 \text{ cm}, \quad CB = 20 \sin 74.2^\circ \approx 19.24 \text{ cm}. \] The two solutions correspond to two congruent right triangles (the roles of \(AB\) and \(CB\) are swapped).