Maximum Area of Rectangle in a Right Triangle - Problem with Solution
Maximize the area of a rectangle inscribed in a right triangle using the first derivative. The problem and its solution are presented
Problem with Solution
BDEF is a rectangle inscribed in the right triangle ABC whose side lengths are 40 and 30. Find the dimensions of the rectangle BDEF so that its area is maximum.

Solution to Problem:
Let the length BF of the rectangle be \( y \) and the width BD be \( x \). The area of the right triangle is given by \( \frac{1}{2} \times 40 \times 30 = 600 \). But the area of the right triangle may also be calculated as the sum of the areas of triangle BEC and BEA. Hence
\[ 600 = \frac{1}{2} \times 40 \times y + \frac{1}{2} \times 30 \times x \]
Let \( A \) be the area of the rectangle. Hence
\[ A = y \times x \]
We now use the first equation to express \( y \) in terms of \( x \) as follows
\[ y = \frac{600 - 15x}{20} \]
Substitute in \( A \) to obtain
\[ A(x) = \frac{x(600 - 15x)}{20} \]
The graph of \( A(x) \) as a function of \( x \) is shown below. \( A(x) \) has a maximum value for \( x = 20 \). This will be shown analytically as well

An expansion of \( A(x) \) shows that \( A(x) \) is a quadratic function with negative leading coefficient and therefore has a maximum value.
\[ A(x) = -\frac{3}{4}x^2 + 30x \]
We now calculate the first derivative of \( A \).
\[ A'(x) = -\frac{3}{2}x + 30 \]
Set \( A'(x) = 0 \) and solve for \( x \).
\[ x = 20 \]
It is easy to check that \( A'(x) \) is positive for \( x \lt 20 \) and negative for \( x > 20 \) and therefore \( A(x) \) has a maximum at \( x = 20 \).
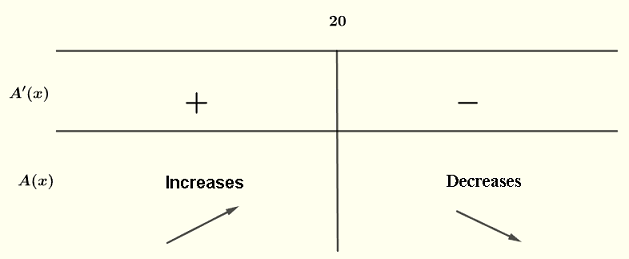
The maximum area is given by \( A(20) \)
\[ A(20) = -\frac{3}{4} \times 20^2 + 30 \times 20 = 300 \]
We now find \( y \) as follows
\[ A = 300 = x \times y , \quad y = \frac{300}{20} = 15 \]
The dimensions of the rectangle that make its area maximum are \( x = 20 \) and \( y = 15 \).
More references and Links
calculus problems



