Differentiation is used to analyze key properties of quadratic functions such as intervals of increase and decrease, local maxima, and local minima.
Quadratic functions in their general form are written as:
\[ f(x) = a x^2 + b x + c \]where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are real numbers with \(a \neq 0\).
The first derivative of \(f\) is:
\[ f'(x) = 2 a x + b \]To determine the maximum or minimum points and intervals of increase or decrease, analyze the sign of \(f'(x)\). The derivative is positive if:
\[ 2 a x + b > 0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad 2 a x > -b \]We consider two cases based on the sign of \(a\):
Dividing both sides of the inequality by \(2a > 0\), we get:
\[ x > -\dfrac{b}{2a} \]The table below summarizes the sign of \(f'(x)\) and whether \(f\) is increasing or decreasing:

Thus, the quadratic function has a minimum at \(\left(-\dfrac{b}{2a}, f\left(-\dfrac{b}{2a}\right)\right)\), decreases on \((-\infty, -\dfrac{b}{2a})\), and increases on \(\left(-\dfrac{b}{2a}, +\infty\right)\).
Dividing both sides by \(2a < 0\) reverses the inequality:
\[ x < -\dfrac{b}{2a} \]The sign of \(f'(x)\) is analyzed using the following table:

In this case, the quadratic function has a maximum at \(\left(-\dfrac{b}{2a}, f\left(-\dfrac{b}{2a}\right)\right)\), increases on \((-\infty, -\dfrac{b}{2a})\), and decreases on \(\left(-\dfrac{b}{2a}, +\infty\right)\).
Quadratic functions in vertex form are written as:
\[ f(x) = a (x - h)^2 + k \]where \(a \neq 0\), and \(h, k\) are real numbers.
The derivative is:
\[ f'(x) = 2 a (x - h) \]We analyze the sign of \(f'(x)\) by considering:
\[ a (x - h) > 0 \]Dividing both sides by \(a > 0\):
\[ x > h \]Use the following table to analyze the sign:
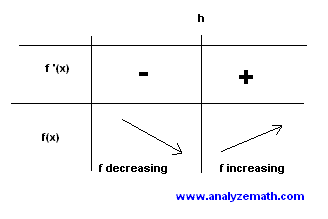
Therefore, the quadratic has a minimum at \((h, k)\), decreases on \((-\infty, h)\), and increases on \((h, +\infty)\).
Dividing both sides by \(a < 0\) reverses the inequality:
\[ x < h \]The sign of \(f'(x)\) is analyzed using:

Here, the quadratic has a maximum at \((h, k)\), increases on \((-\infty, h)\), and decreases on \((h, +\infty)\).
Find the extremum (minimum or maximum) of the quadratic function:
\[ f(x) = 2x^2 - 8x + 1 \]
Find the extremum of the quadratic function:
\[ f(x) = - (x + 3)^2 + 1 \]
For each quadratic function below, find the extremum (minimum or maximum), the interval of increase, and the interval of decrease:
See more about applications of differentiation.