
A critical point of a multivariable function is a point where the partial derivatives of first order of this function are equal to zero. Examples with detailed solution on how to find the critical points of a function with two variables are presented.
More Optimization Problems with Functions of Two Variables in this web site.
Solution to Example 1:
We first find the first order partial derivatives.
\( f_x(x,y) = 2x \)
\( f_y(x,y) = 2y \)
We now solve the following equations \( f_x(x,y) = 0 \) and \( f_y(x,y) = 0 \) simultaneously.
\( f_x(x,y) = 2x = 0 \)
\( f_y(x,y) = 2y = 0 \)
The solution to the above system of equations is the ordered pair (0,0).
Below is the graph of \( f(x , y) = x^2 + y^2 \) and it looks that at the critical point (0,0) \( f \) has a minimum value.

Solution to Example 2:
Find the first order partial derivatives of function \( f \).
\( f_x(x,y) = 2x \)
\( f_y(x,y) = -2y \)
Solve the following equations \( f_x(x,y) = 0 \) and \( f_y(x,y) = 0 \) simultaneously.
\( f_x(x,y) = 2x = 0 \)
\( f_y(x,y) = - 2y = 0 \)
The solution is the ordered pair (0,0).
The graph of \( f(x , y) = x^2 - y^2 \) is shown below. \( f \) is curving down in the y direction and curving up in the x direction. \( f \) is stationary at the point (0,0) but there is no extremum (maximum or minimum). (0,0) is called a saddle point because there is neither a relative maximum nor a relative minimum and the surface close to (0,0) looks like a saddle.

Solution to Example 3:
We first find the first order partial derivatives.
\( f_x(x,y) = - 2x \)
\( f_y(x,y) = - 2y \)
We now solve the following equations \( f_x(x,y) = 0 \) and \( f_y(x,y) = 0 \) simultaneously.
\( f_x(x,y) = - 2x = 0 \)
\( f_y(x,y) = - 2y = 0 \)
The solution to the above system of equations is the ordered pair (0,0).
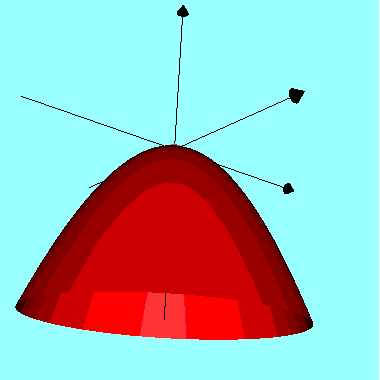
The graph of \( f(x , y) = - x^2 - y^2 \) is shown below and it has a relative maximum.
Solution to Example 4:
The first order partial derivatives are given by
\( f_x(x,y) = 3x^2 + 6x - 9 \)
\( f_y(x,y) = 3y^2 - 12 \)
We now solve the equations \( f_x(x,y) = 0 \) and \( f_y(x,y) = 0 \) simultaneously.
\( 3x^2 + 6x - 9 = 0 \)
\( 3y^2 - 12 = 0 \)
The solutions, which are the critical points, to the above system of equations are given by
(1,2) , (1,-2) , (-3,2) , (-3,-2)