 .
.
Are you looking to master exponential equations? This guide provides Grade 12 students with clear, detailed solutions using both analytical and graphical methods. You'll learn powerful techniques such as substitution and the rules of exponential and logarithmic functions to solve complex equations with confidence.
We also show how to solve exponential equations graphically. To do this, we first rewrite the equation in the form \( f(x) - g(x) = 0 \). Then, we graph the function \( f(x) - g(x) \), and the x-intercepts of the graph represent the solutions to the original equation.
Whether you're preparing for exams or just want to strengthen your math skills, this resource will help you understand and solve exponential equations step by step.
Note that 27, 9 and 3 may be written as powers of 3 as follows:
\[ 27 = 3^3, \quad 9 = 3^2, \quad \text{and} \quad 3 = 3^1 \] Using the above and also the formula for negative exponent \[ \dfrac{1}{x^n} = x^{-1} \]We rewrite the given equation as follows: \[ (3^3)^{2x} \cdot (3^{-2})^{x - 2} = (3^2)^{-x} \cdot (3^{-1})^{2 - x} \]
We now use the formula \((x^m)^n = x^{mn}\) to rewrite the above equation as follows. \[ 3^{6x} \cdot 3^{-2x + 4} = 3^{-2x} \cdot 3^{-2 + x} \]
Use the formula \(x^m \cdot x^n = x^{m + n}\) to rewrite the equation as follows \[ 3^{6x - 2x + 4} = 3^{-2x - 2 + x} \]
Simplify the exponents to obtain \[ 3^{4x + 4} = 3^{-x - 2} \]
We use the fact that an exponential function of the form \(a^x\) is a one-to-one function, meaning that if \(3^m = 3^n\), then \(m = n\) to write an algebraic equation using the above equation: \[ 4x + 4 = -x - 2 \]
Solve the above for \(x\) to obtain the solution of the given equation.
\[
5x = -6 \quad \text{gives the solution} \quad x = \dfrac{-6}{5} = -1.2
\]
Below is shown the graph of the left side of the given equation when written with right side equal to zero as follows:
\[ 27^{2x} \left(\dfrac{1}{9}\right)^{x-2} - 9^{-x} \left(\dfrac{1}{x}\right)^{2-x} = 0 \]
The x intercept is an approximation to the analytical solution found above. Check that they are close in value.
 .
.
Note that \( \sqrt{16^x} = (16^x)^{1/2} = 16^{(1/2)x} \) and use it to rewrite the given equation as \[ 16^{(1/2)x} = \left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{x^2 - 1} \]
Note that \( \dfrac{1}{2} = 2^{-1} \) and \( 16 = 2^4 \) and use it to rewrite the above equation as \[ (2^4)^{(1/2)x} = (2^{-1})^{x^2 - 1} \]
Use the formula \( (x^m)^n = x^{mn} \) to rewrite the above equation as \[ 2^{2x} = 2^{-x^2 + 1} \]
We use the fact that an exponential function of the form \( a^x \) is a one-to-one function to write \[ 2x = -x^2 + 1 \]
Rewrite in standard form and solve the above quadratic equation. \[ x^2 + 2x - 1 = 0 \] \[ \Delta = 2^2 - 4(1)(-1) = 8 \]
Two solutions: \( x_1 = -1 - \sqrt{2} \approx -2.41 \) and \( x_2 = -1 + \sqrt{2} \approx 0.41 \)
The graph of the left side of the given equation when written with the right side equal to zero as follows:
\[ \sqrt{16^x} - \left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)^{x^2-1} = 0 \]is shown below. The x-intercepts are approximations to the analytical solutions found above. Check that they have close values.
 .
.
What are the solutions to the equation \[ 2^x - 6 \cdot 2^{-x} = 6 \;\; ? \]
Let \( u = 2^x \) which also gives \( \dfrac{1}{u} = 2^{-x} \), and rewrite the equation in terms of \( u \). [ u - \dfrac{6}{u} = 6 \]
\( u \) cannot be zero ( because \( 2^x \) cannot be less than or equal to zero ), we therefore multiply all terms of the above equation by \( u \) and simplify. \[ u \left( u - \dfrac{6}{u} \right) = 6u \] \[ u^2 - 6 = 6u \] \[ u^2 - 6u - 6 = 0 \]
Solve the above quadratic equation for \( u \) to obtain two solutions: \[ u_1 = 3 + \sqrt{15} \quad \text{and} \quad u_2 = 3 - \sqrt{15} \]
We now solve for \( x \) using the above substitution \( u = 2^x \).
First equation: \( 2^x = 3 + \sqrt{15} \) \[ \ln(2^x) = \ln(3 + \sqrt{15}) \] \[ x \ln(2) = \ln(3 + \sqrt{15}) \] \[ x = \dfrac{\ln(3 + \sqrt{15})}{\ln 2} \approx 2.78 \]
Second equation: \( 2^x = 3 - \sqrt{15} \) has no solution because \( 3 - \sqrt{15} \) is less than zero.
Below is shown the graph of the left side of the given equation when written with right side equal to zero as follows: \( 2^x - 6 \cdot 2^{-x} - 6 = 0 \). The \( x \)-intercept is an approximation to the solution of the analytical solution found above.
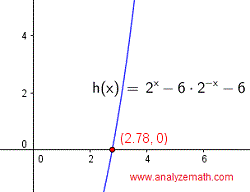 .
.
Find the solutions to the equation \[ 5^{x+1} = 100 \cdot 3^x \]
Take the natural logarithm (\ln) of both sides of the given equation: \[ \ln(5^{x + 1}) = \ln(100 \cdot 3^x) \]
Use log rules to simplify. \[ (x + 1) \ln 5 = \ln 100 + x \ln 3 \]
Expand left side and group terms with x \[ x \ln 5 + \ln 5 = \ln 100 + x \ln 3 \] \[ x (\ln 5 - \ln 3) = \ln 100 - \ln 5 \]
Solve for \(x \). \[ x = \dfrac{\ln 100 - \ln 5}{\ln 5 - \ln 3} \approx 5.86 \]
Below is shown the graph of the left side of the given equation when written with right side equal to zero as follows:
\[ 5^{x+1} - 100 \cdot 3^x = 0 \]The x-intercept is an approximation to the solution of the analytical solution found above.
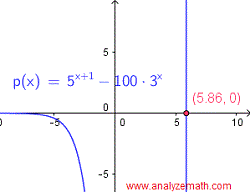 .
.
Solve the equation \[ \dfrac{e^x - e^{-x}}{2} = 3 \]
Let \( u = e^x \), which also gives \( \dfrac{1}{u} = e^{-x} \), and rewrite the equation in \( u \). \( u = e^x \) cannot be less than or equal to zero. \[ \dfrac{u - \dfrac{1}{u}}{2} = 3 \]
Multiply both sides by 2 and simplify: \[ u - \dfrac{1}{u} = 6 \]
Multiply both sides by \( u \) and simplify: \[ u^2 - 1 = 6u \] \[ u^2 - 6u - 1 = 0 \]
Solve for \( u \) to obtain two solutions: \[ u_1 = 3 + \sqrt{10} \quad \text{and} \quad u_2 = 3 - \sqrt{10} \]
We now solve for \( x \) using the above substitution \( u = e^x \). First equation: \[ e^x = 3 + \sqrt{10} \] Take the \( \ln \) of both sides: \[ \ln(e^x) = \ln(3 + \sqrt{10}) \]
Simplify to solve: \[ x = \ln(3 + \sqrt{10}) \approx 1.82 \]
Second equation: \( e^x = 3 - \sqrt{10} \) has no solution because \( 3 - \sqrt{10} \) is less than zero.
Below is shown the graph of the left side of the given equation when written with right side equal to zero as follows:
\[ \dfrac{e^x - e^{-x}}{2} - 3 = 0 \]
The x intercept is an approximation to the solution of the analytical solution found above.
 .
.
What are the solutions to the equation \[ 3^{2-3x} = 4^{2x+1} \; \; ?\]
Take the natural logarithm (ln) of both sides \[ \ln(3^{2 - 3x}) = \ln(4^{2x + 1}) \]
Use log rules to simplify. \[ (2 - 3x)\ln 3 = (2x + 1)\ln 4 \]
Expand both sides of the equation and group terms with \( x \).
\[ 2\ln 3 - 3x\ln 3 = 2x\ln 4 + \ln 4 \] \[ x(-3\ln 3 - 2\ln 4) = \ln 4 - 2\ln 3 \] \[ x = \dfrac{2\ln 3 - \ln 4}{3\ln 3 + 2\ln 4} \approx 0.13 \]Take the natural logarithm (ln) of both sides
\[ \ln(3^{2 - 3x}) = \ln(4^{2x + 1}) \]Use log rules to simplify.
\[ (2 - 3x)\ln 3 = (2x + 1)\ln 4 \]Expand both sides of the equation and group terms with \( x \).
\[ 2\ln 3 - 3x\ln 3 = 2x\ln 4 + \ln 4 \] \[ x(-3\ln 3 - 2\ln 4) = \ln 4 - 2\ln 3 \] \[ x = \dfrac{2\ln 3 - \ln 4}{3\ln 3 + 2\ln 4} \approx 0.13 \] .
.
Note that
\[ 9^x = (3^2)^x = 3^{2x} = (3^x)^2 \]Rewrite the given equation using \( 9^x = (3^x)^2 \) and also \( 3^{x + 1} = 3 \cdot 3^x \)
\[ (3^x)^2 - 3 \cdot 3^x + 2 = 0 \]Let \( u = 3^x \) and rewrite the equation in \( u \).
\[ u^2 - 3u + 2 = 0 \]Solve for \( u \) by factoring
\[ (u - 2)(u - 1) = 0 \]Two solutions: \( u_1 = 2 \) and \( u_2 = 1 \)
We now solve for \( x \) using the above substitution \( u = 3^x \).
First equation: \( 3^x = 2 \)
\[ \ln(3^x) = \ln 2 \] \[ x \ln 3 = \ln 2 \] \[ x = \dfrac{\ln 2}{\ln 3} \approx 0.63 \]Second equation: \( 3^x = 1 \), solution \( x = 0 \).
 .
.