Grade 12 trigonometry problems and questions with solutions are presented.
Questions 1
Prove the identity \[ \tan^2(x) - \sin^2(x) = \tan^2(x) \sin^2(x) \]
We start with the left hand side of the given identity
Use the identity \( \tan(x) = \dfrac{\sin(x)}{\cos(x)} \) in the left hand side of the given identity to write: \[ \tan^2(x) - \sin^2(x) = \left(\dfrac{\sin(x)}{\cos(x)}\right)^2 - \sin^2(x) \] \[ = \dfrac{\sin^2(x)}{\cos^2(x)} - \sin^2(x) \] \[ = \dfrac{\sin^2(x) - \cos^2(x) \sin^2(x)}{\cos^2(x)} \] \[ = \dfrac{\sin^2(x) \left(1 - \cos^2(x)\right)}{\cos^2(x)} \] \[ = \dfrac{ \sin^2(x) \sin^2(x)}{\cos^2(x)} \] \[ = \sin^2(x) \tan^2(x) \] which is equal to the right hand side of the given identity.
Questions 2
Prove the identity \[ \dfrac{1 + \cos(x) + \cos(2x)}{\sin(x) + \sin(2x)} = \cot(x) \]
Use the identities \( \cos(2x) = 2 \cos^2(x) - 1 \) and \( \sin(2x) = 2 \sin(x) \cos(x) \) in the left hand side of the given identity to write: \[ \dfrac{1 + \cos(x) + \cos(2x)}{\sin(x) + \sin(2x)} \] \[ = \dfrac{1 + \cos(x) + 2 \cos^2(x) - 1}{\sin(x) + 2 \sin(x) \cos(x) } \] \[ = \dfrac{\cos(x) + 2 \cos^2(x)}{\sin(x) + 2 \sin(x) \cos(x) } \] \[ = \dfrac{\cos(x) (1 + 2 \cos(x))}{\sin(x) (1 + 2 \cos(x)) } \] \[ = \dfrac{\cos(x)}{\sin(x)} \] \[ = \cot(x) \] which is equal to the right hand side of the given identity.
Questions 3
Prove the identity \[ 4 \sin(x) \cos(x) = \dfrac{\sin(4x)}{\cos(2x)} \]
Use the identity \( \sin(2x) = 2 \sin(x) \cos(x) \) to write \( \sin(4x) = 2 \sin(2x) \cos(2x) \) in the right hand side of the given identity to write: \[ \dfrac{\sin(4x)}{\cos(2x)} = \dfrac{2 \sin(2x) \cos(2x)}{\cos(2x)}\] \[ = 2 \sin(2x) \] \[ = 2 \times 2 \sin(x) \cos(x) \] \[ = 4 \sin(x) \cos(x) \] which is equal to the left hand side of the given identity.
Questions 4
Solve the trigonometric equation \[ \sin(x) + \sin(x/2) = 0 \quad \text{for} \quad 0 \le x \le 2 \pi \]
Use the identity \( \sin(2x) = 2 \sin(x) \cos(x) \) to write \( \sin(x) \) as
\[ \sin(x) = \sin(2 ( x/2 ) ) = 2 \sin(x / 2) \cos(x / 2) \]
and use in the right hand side of the given equation to write it as follows
\[ 2 \sin(x / 2) \cos(x / 2) + \sin(x / 2) = 0 \]
Factor \( \sin(x / 2) \)
\[ \sin(x/2) ( 2 \cos(x/2) + 1 ) = 0 \]
which gives two equations to solve
\[ \sin(x/2) = 0 \quad \text{and} \quad 2 \cos(x/2) + 1 = 0 \]
a) The equation \( \sin(x / 2) = 0 \) has the solutions \( x / 2 = 0 \) and \( x / 2 = \pi \)
Solve for \( x \) to obtain the solutions: \( x = 0 \) and \( x = 2 \pi \)
b) The equation \( 2 \cos(x/2) + 1 = 0 \) may be written as \[ \cos(x/2) = -1/2 \] which has the solutions \( x/2 = 2 \pi/3 \) and \( x/2 = 4 \pi/3 \)
Solve for \( x \) to obtain the solutions: \( x = 4 \pi/3 \) and \( x = 8 \pi/3 \)
Note that \( 8 \pi/3 \) is greather than \( 2 \pi \) and is therefore not accepted.
Final solutions for the given equation are: \( \{ 0 , 4 \pi/3 , 2 \pi \} \)
Questions 5
Solve the trigonometric equation \[ (2\sin(x) - 1)(\tan(x) - 1) = 0 \quad \text{for} \quad 0 \le x \le 2 \pi \]
The given equation is already in factored form \[ (2\sin(x) - 1)(\tan(x) - 1) = 0 \] which leads to two equations to solve: \[ 2\sin(x) - 1 = 0 \quad \text{and} \quad \tan(x) - 1 = 0 \] The above equations may be written as \[ \sin(x) = 1/2 \quad \text{and} \quad \tan(x) = 1 \] The solutions of the equation \( \sin(x) = 1/2 \) are: \[ x = \pi/6 \quad \text{and} \quad x = 5 \pi/6 \] The solutions of the equation \( \tan(x) = 1 \) are: \[ x = \pi /4 \quad \text{and} \quad x = 5 \pi/4 \] The solutions of the given equation within the given interval are: \[ \{\pi/6, 5 \pi/6 , \pi /4 , 5 \pi/4 \} \]
Questions 6
Solve the trigonometric equation \[ \cos(2x) \cos(x) - \sin(2x) \sin(x) = 0 \quad \text{for} \quad 0 \le x \le 2 \pi \]
Use the formula for \( \cos(A + B) \) to write \[ \cos(3x) = \cos(2x + x) = \cos(2x) \cos(x) - \sin(2x) \sin(x) \] . Hence the given equation \[ \cos(2x) \cos(x) - \sin(2x) \sin(x) = 0 \] may be written as \[ \cos(3x) = 0 \] Solve the above equation for \( 3x \) to obtain: \[ 3x = \pi/2 \quad \text{,} \quad 3x = 3\pi/2 \quad \text{,} \quad 3x = 5\pi/2 \quad \text{,} \quad 3x = 7\pi/2 \quad \text{,} \quad 3x = 9\pi/2 \quad \text{and} \quad 3x = 11\pi/2 \] Solve the above for \( x \) to obtain the solutions: \[ \{\pi/6, \pi/2, 5\pi/6, 7\pi/6, 3\pi/2 , 11\pi/6 \} \]
Questions 7
Simplify the trigonometric expression \[ \dfrac{\sin(2x) - \cos(x)}{\cos(2x) + \sin(x) - 1 } \]
Use the identities \( \sin(2x) = 2 \sin(x) \cos(x) \) and \( \cos(2x) = 1 - 2 \sin^2(x) \) to rewrite the given expression as follows \[ \dfrac{\sin(2x) - \cos(x)}{\cos(2x) + \sin(x) - 1 } = \dfrac{ 2 \sin(x) \cos(x) - \cos(x)}{1 - 2 \sin^2(x) + \sin(x) - 1 } \] Simplify the right hand side and factor numerator and denominator \[ = \dfrac{\cos(x)( 2 \sin(x) -1) }{ \sin(x)( - 2 \sin(x) + 1) } \] Simplify \[ = - \dfrac{\cos(x)}{ \sin(x)} \] \[ = - \cot(x) \]
Questions 8
Prove that \[ \sin(105^{\circ}) = \dfrac{\sqrt 6 + \sqrt 2}{4} \]
\( 105^{\circ} \) may be written as the sum of two special angles as follows: \[ 105^{\circ} = 60^{\circ} + 45^{\circ}\] Hence \[ \sin(105^{\circ}) = \sin(60^{\circ} + 45^{\circ}) \] Use the identities \( \sin(a + b) = \sin(a)\cos(b) + \cos(a)\sin(b) \) to write \[ \sin(105^{\circ}) = \sin(60^{\circ})\cos(45^{\circ}) + \cos(60^{\circ}) \sin(45^{\circ}) \] Use table of special angles \[ = (\sqrt {3} / 2 )(\sqrt {2}/2) + (1/2)(\sqrt {2}/2) \] \[ = \dfrac{ \sqrt {6} + \sqrt {2} } {4} \]
Questions 9
If \( \sin(x) = \dfrac{2}{5}\) and x is an acute angle, find the exact values of
- ) \( \cos(2x) \)
- ) \( \cos(4x) \)
- ) \( \sin(2x) \)
- ) \( \sin(4x) \)
If \( \sin(x) = 2/5 \) then \( \cos(x) = \sqrt {1 - \sin^2 x} = \sqrt{1 - (2/5)^2} = \sqrt{21}/5 \)
- ) Use identity: \( \cos(2x) = 1 - 2 \sin^2(x) = 17/25 \)
- ) Use identity: \[ \cos(4x) = 1 - 2 \sin^2(2 x) \] \[ = 1 - 2 [ 2\sin(x) \cos(x) ]^2 \] \[ = 457 / 625 \]
- ) Use identity: \[ \sin(2x) = 2 \sin(x) \cos(x) = 4 \sqrt{21}/25 \]
- ) Use identity: \[ \sin(4x) = \sin(2(2x)) = 2 \cos(2x) \sin(2x) \] \[ = 2 (17/25)(4 \sqrt{21}/25) = 136 \sqrt{21} / 625 \]
Questions 10
Find the length of side AB in the figure below. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.
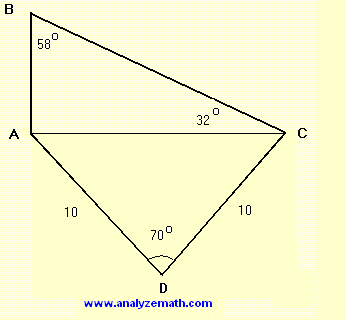 .
.
Note that triangle \( DAC \) is isosceles and therefore if we draw the perpendicular from D to AC, it will cut AC into two halves and bisect angle D. Hence
