Sine Functions: Maximum and Minimum – Problems
This tutorial explains the relationship between the amplitude, the vertical shift, and the maximum and minimum values of the
sine function.
Problem 1
Function \( F \) is a sine function defined by
\[
F(x) = a\sin(bx + c) + d,
\]
with \( a > 0 \).
- Show that the maximum value \( F_{\max} \) and the minimum value \( F_{\min} \) of \( F(x) \) are
\[
F_{\max} = d + a, \qquad F_{\min} = d - a.
\]
- Show that
\[
d = \frac{F_{\max} + F_{\min}}{2}.
\]
- Show that
\[
a = \frac{F_{\max} - F_{\min}}{2}.
\]
Solution to Problem 1
-
We start by using the fact that
\[
-1 \le \sin(bx + c) \le 1.
\]
-
Multiply all terms of the above double inequality by \( a \):
\[
-a \le a\sin(bx + c) \le a.
\]
-
Add \( d \) to all terms of the inequality:
\[
d - a \le a\sin(bx + c) + d \le d + a.
\]
-
Since \( a\sin(bx + c) + d = F(x) \), we obtain
\[
d - a \le F(x) \le d + a.
\]
-
Therefore, the minimum and maximum values of \( F(x) \) are
\[
F_{\min} = d - a, \qquad F_{\max} = d + a.
\]
-
Add the equations \( F_{\max} = d + a \) and \( F_{\min} = d - a \):
\[
F_{\max} + F_{\min} = 2d.
\]
-
Divide both sides by 2 to obtain
\[
d = \frac{F_{\max} + F_{\min}}{2}.
\]
-
Add the equations \( F_{\max} = d + a \) and \( -F_{\min} = -d + a \):
\[
F_{\max} - F_{\min} = 2a.
\]
-
Divide both sides by 2 to obtain
\[
a = \frac{F_{\max} - F_{\min}}{2}.
\]
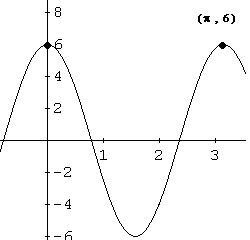
Problem 2
The graph of the sine function \( F \) defined by
\[
F(x) = a\sin(x) + d,
\]
with \( a > 0 \), is shown below.
Use the graph and the results of Problem 1 to find \( a \) and \( d \).
Solution to Problem 2
-
From the graph, the maximum value is \( F_{\max} = 6 \) and the minimum value is \( F_{\min} = -2 \).
-
Using the formulas from Problem 1:
\[
d = \frac{F_{\max} + F_{\min}}{2} = \frac{6 + (-2)}{2} = 2,
\]
and
\[
a = \frac{F_{\max} - F_{\min}}{2} = \frac{6 - (-2)}{2} = 4.
\]
Problem 3
Find \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) included in the definition of the sine function \( f \) given by
\[
f(x) = a \sin(bx + c)
\]
such that the maximum value of \( f(x) \) is 6, \( f(0) = 6 \), and the period of the graph of
function \( f \) is equal to \( \pi \).
The constants \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are positive and \( c < 2\pi \).
Solution to Problem 3
-
The maximum value 6 gives the amplitude
\[
|a| = 6
\]
-
Solve the above equation for \( a \) and select the positive value.
\[
a = 6
\]
-
The period may be used to find \( b \) using
\[
\text{Period} = \frac{2\pi}{|b|} = \pi
\]
-
Solve for \( |b| \)
\[
|b| = 2
\]
-
Solve for \( b \) and select the positive value
\[
b = 2
\]
-
Substitute 6 for \( a \) in the formula of the function and use \( f(0) = 6 \)
to write an equation in \( c \).
\[
6 = 6 \sin(2 \cdot 0 + c)
\]
-
Which gives
\[
\sin(c) = 1
\]
-
Solve for \( c \)
\[
c = \frac{\pi}{2} + k(2\pi), \quad \text{where } k \text{ is an integer}
\]
There is an infinite number of solutions for \( c \).
-
Select \( k = 0 \) since it is the only value that gives
\( 0 < c < 2\pi \), which gives
\[
c = \frac{\pi}{2}
\]
-
Function \( f \) is given by
\[
f(x) = 6 \sin\left(2x + \frac{\pi}{2}\right)
\]
-
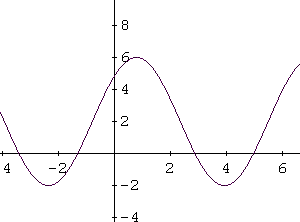
For checking, part of the graph of \( f \) is shown below.
Check the period, verify that \( f(0) = 6 \),
and confirm that the maximum value of \( f(x) \) is 6.
More References and Links
Trigonometry Problems
Match Sine Functions to Graphs