Our students, at UGRU, have difficulties in reading with understanding and extracting the information from the text of the problem. This skill has to be taught explicitly to our students. It is the first step in problem solving and students cannot make any progress if the problem is not understood.
3.3 Thinking and Reasoning in Problem SolvingCritical thinking is needed in all steps of problem solving. Students do not look back critically at the solution of a problem once it is solved. They tend to accept whatever answer they have obtained. Critical thinking is needed when extracting information from the text of the problem, formulating and solving the problem and analyzing the solution obtained. I now give an example of a problem that may be used to give opportunities to students to think critically.
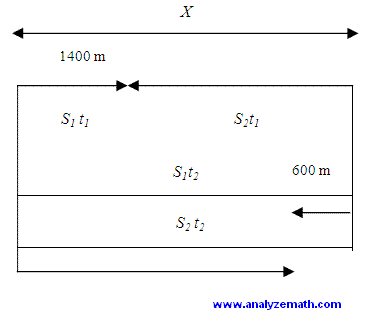
Problem 6: Two boats on opposite banks of a river start moving towards each other. They first pass each other 1400 meters from one bank. They each continue to the opposite bank, immediately turn around and start back to the other bank. When they pass each other a second time, they are 600 meters from the other bank. We assume that each boat travels at a constant speed all along the journey. Is it possible to find the width of the river using the given information?
Students are guided to make a diagram and write the equations to formulate the problem.(see solution in appendix A)Let t = 0 be the time when the two boats start moving. Let S1 and S2 be the constant speeds of the two boats and t1 the time when they first pass each other and t2 the time when they pass each other for the second time. Let X the width of the river.

S1t1 = 1400
1400 + S2 t1 = X
S1 t2 = X + 600
S2 t2 = 2X - 600
Because there are five unknowns and only four equations in the above system of equations, students are tempted to say that it is not possible to find the width X of the river. This particular problem can be used to generate activities where students will have to think in order to come up with a correct answer to the question in the problem. Enough time should be given to students to discuss such a challenging problem. They should be allowed to work in groups and if students cannot finish the work in class, they should be allowed to continue solving the problem as a homework assignment. Students will not benefit if the solution is given to them without giving them enough time to investigate this type of problems. Learning will take place through the time and efforts spent on finding a solution even if they have difficulties finding one. These types of problems involve a lot of thinking both to understand the problem and to come up with a solution and they are necessary if we want our students to develop their thinking skills to the highest level possible and become genuine problem solvers.
It is not difficult to design problems that can activate students thinking. One has to avoid problems with one obvious solution. Note that the question in problem 6 does not say “find the width of the river” but “is it possible to find the width of the river using the given information?”. A question of the type “find the width of the river” already assumes that it is possible to find the width X. However questions of the second type are more demanding and therefore suitable to develop thinking skills.
Open ended problems, usually with many valid answers, can also be used as tools to generate activities where students have to think in order to come with answers. Useful discussions can be generated in order to compare all valid answers generated by students. I now give an example of an open ended problem.
Problem 7: Create a set of data points that satisfies the following conditions:
• The set includes 8 data values.
• The range of the data set is 20.
• The median is equal to the mean.
Show that your data set satisfies the conditions.
Logical reasoning is fundamental to success in mathematics in general and problem solving in particular. Inductive reasoning uses easy to understand cases to identify patterns and it can also be used to establish relationships between mathematical objects. Deductive reasoning uses mathematical definitions, axioms, rules and theorems to draw conclusions. Deductive reasoning is fundamental to critical thinking. Geometry problems may be used as tools to develop deductive reasoning [14]. I believe that both must be used and explicitly discussed with students.
Home Page