Question
Two dice are tossed. What is the probability that the sum of the two dice is greater than 3?
Solution
When two dice are tossed, there are \(6 \times 6 = 36\) possible outcomes.
The outcomes that give a sum of 3 or less are: \((1,1), (1,2), (2,1)\).
There are \(36 - 3 = 33\) outcomes with a sum greater than 3.
The probability is: \[\frac{33}{36} = \frac{11}{12}\]
Question
If L is a line through the points \((2,5)\) and \((4,6)\), what is the value of \(k\) so that the point \((7,k)\) is on the line L?
Solution
The slope of the line through \((2,5)\) and \((4,6)\) is:
\[m = \frac{6 - 5}{4 - 2} = \frac{1}{2}\]
The slope through \((4,6)\) and \((7,k)\) is:
\[m = \frac{k - 6}{7 - 4} = \frac{k - 6}{3}\]
Since all three points are collinear, the slopes are equal:
\[\frac{1}{2} = \frac{k - 6}{3}\]
Solving for \(k\): \(3 = 2(k - 6) \Rightarrow 3 = 2k - 12 \Rightarrow 2k = 15 \Rightarrow k = \frac{15}{2}\)
Question
Find a negative value of \(k\) so that the graph of \(y = x^2 - 2x + 7\) and the graph of \(y = kx + 5\) are tangent.
Solution
Set the equations equal to find intersection points:
\[x^2 - 2x + 7 = kx + 5\]
Rearrange: \(x^2 - (2 + k)x + 2 = 0\)
For tangency, the discriminant must be zero:
\[(2 + k)^2 - 4(1)(2) = 0\]
\[(2 + k)^2 = 8\]
\[2 + k = \pm 2\sqrt{2}\]
\[k = -2 \pm 2\sqrt{2}\]
The negative solution is: \(k = -2 - 2\sqrt{2}\)
Question
Which of these graphs is closest to the graph of \(f(x) = \frac{|4 - x^2|}{x + 2}\)?
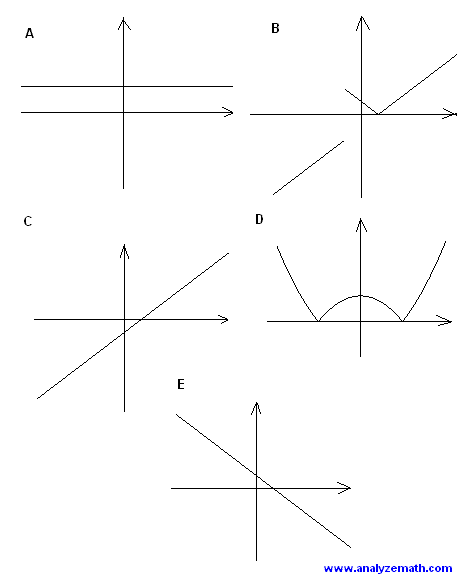
Solution
Function \(f(x) = \frac{|4 - x^2|}{x + 2}\) is undefined at \(x = -2\). Graph B is the only one undefined at a negative x-value.
Question
The circle \((x - 3)^2 + (y - 2)^2 = 1\) has center C. Point \(M(4,2)\) is on the circle. N is another point on the circle so that angle MCN = 30°. Find the coordinates of N.
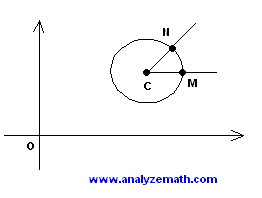
Solution
Center C from equation: \(C(3, 2)\)
Vector OC: \(\langle 3, 2 \rangle\)
Vector CN (radius = 1, angle 30°): \(\langle \cos 30^\circ, \sin 30^\circ \rangle = \langle \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}, \frac{1}{2} \rangle\)
Vector ON = OC + CN: \(\langle 3 + \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}, 2 + \frac{1}{2} \rangle = \langle 3 + \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}, \frac{5}{2} \rangle\)
Coordinates of N: \(\left( 3 + \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}, \frac{5}{2} \right)\)
Question
Vectors \(\mathbf{u} = \langle 2, 0 \rangle\) and \(\mathbf{v} = \langle -3, 1 \rangle\). What is the length of \(\mathbf{w} = -\mathbf{u} - 2\mathbf{v}\)?
Solution
Calculate \(\mathbf{w}\):
\[\mathbf{w} = -\langle 2, 0 \rangle - 2\langle -3, 1 \rangle = \langle -2, 0 \rangle + \langle 6, -2 \rangle = \langle 4, -2 \rangle\]
Length of \(\mathbf{w}\):
\[\sqrt{4^2 + (-2)^2} = \sqrt{16 + 4} = \sqrt{20} = 2\sqrt{5}\]
Question
What is the smallest distance between the point \((-2,-2)\) and a point on the circle \((x - 1)^2 + (y - 2)^2 = 4\)?
Solution
Circle center \(C(1,2)\), radius \(r=2\)
Distance from point to center:
\[OC = \sqrt{(-2-1)^2 + (-2-2)^2} = \sqrt{(-3)^2 + (-4)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = 5\]
Point is outside circle. Smallest distance:
\[5 - 2 = 3\]
Question
What is the equation of the horizontal asymptote of \(f(x) = \frac{2}{x + 2} - \frac{x + 3}{x + 4}\)?
Solution
As \(x \to \pm\infty\), \(\frac{2}{x+2} \to 0\) and \(-\frac{x+3}{x+4} \to -1\).
Thus horizontal asymptote: \(y = -1\).
Question
The lines \(x + 3y = 2\) and \(-2x + ky = 5\) are perpendicular. Find \(k\).
Solution
Slope of first line: \(3y = -x + 2 \Rightarrow y = -\frac{1}{3}x + \frac{2}{3}\), slope \(m_1 = -\frac{1}{3}\)
Slope of second line: \(ky = 2x + 5 \Rightarrow y = \frac{2}{k}x + \frac{5}{k}\), slope \(m_2 = \frac{2}{k}\)
For perpendicular lines: \(m_1 \cdot m_2 = -1\)
\[-\frac{1}{3} \cdot \frac{2}{k} = -1\]
\[-\frac{2}{3k} = -1\]
\[\frac{2}{3k} = 1\]
\[2 = 3k \Rightarrow k = \frac{2}{3}\]
Question
If \(f(x) = (x - 1)^2\) and \(g(x) = \sqrt{x}\), then \((g \circ f)(x) = ?\)
Solution
Composition definition: \((g \circ f)(x) = g(f(x)) = g((x-1)^2)\)
Apply \(g\): \(\sqrt{(x-1)^2} = |x - 1|\)
Note: \(\sqrt{x^2} = |x|\) not \(x\)
Question
The domain of \(f(x) = \frac{\sqrt{4 - x^2}}{\sqrt{x^2 - 1}}\) is given by which interval?
Solution
Conditions: \(x^2 - 1 > 0\) (denominator positive) and \(4 - x^2 \ge 0\) (numerator real).
1) \(x^2 - 1 > 0 \Rightarrow x < -1\) or \(x > 1\)
2) \(4 - x^2 \ge 0 \Rightarrow -2 \le x \le 2\)
Intersection: \([-2, -1) \cup (1, 2]\)
Question
The area of the circle \(x^2 + y^2 - 8y - 48 = 0\) is:
Solution
Complete the square for \(y\):
\(x^2 + (y^2 - 8y) - 48 = 0\)
\(x^2 + (y^2 - 8y + 16) - 16 - 48 = 0\)
\(x^2 + (y - 4)^2 - 64 = 0\)
\(x^2 + (y - 4)^2 = 64\)
Radius \(R = 8\), area: \(\pi R^2 = 64\pi\)
Question
The y-coordinates of all intersection points of the parabola \(y^2 = x + 2\) and the circle \(x^2 + y^2 = 4\) are:
Solution
Substitute \(y^2 = x + 2\) into circle equation:
\(x^2 + (x + 2) = 4\)
\(x^2 + x - 2 = 0\)
\((x + 2)(x - 1) = 0\)
\(x = -2\) or \(x = 1\)
For \(x = -2\): \(y^2 = -2 + 2 = 0 \Rightarrow y = 0\)
For \(x = 1\): \(y^2 = 1 + 2 = 3 \Rightarrow y = \pm\sqrt{3}\)
y-coordinates: \(-\sqrt{3}, 0, \sqrt{3}\)
Question
What is the smallest positive zero of \(f(x) = \frac{1}{2} - \sin(3x + \frac{\pi}{3})\)?
Solution
Set \(f(x)=0\): \(\sin(3x + \frac{\pi}{3}) = \frac{1}{2}\)
General solutions:
\(3x + \frac{\pi}{3} = \frac{\pi}{6} + 2k\pi\) or \(3x + \frac{\pi}{3} = \frac{5\pi}{6} + 2k\pi\)
Solve first: \(3x = -\frac{\pi}{6} + 2k\pi \Rightarrow x = -\frac{\pi}{18} + \frac{2k\pi}{3}\)
Solve second: \(3x = \frac{\pi}{2} + 2k\pi \Rightarrow x = \frac{\pi}{6} + \frac{2k\pi}{3}\)
For \(k=0\): \(x = -\frac{\pi}{18}\) or \(x = \frac{\pi}{6}\)
Smallest positive zero: \(x = \frac{\pi}{6}\)
Question
If \(x - 1\), \(x - 3\), and \(x + 1\) are all factors of a cubic polynomial \(P(x)\), which must also be a factor?
I) \(x^2 + 1\)
II) \(x^2 - 1\)
III) \(x^2 - 4x + 3\)
Solution
Polynomial form: \(P(x) = k(x-1)(x-3)(x+1)\)
Possible factor combinations:
\((x-1)(x-3) = x^2 - 4x + 3\) (III)
\((x-1)(x+1) = x^2 - 1\) (II)
\((x-3)(x+1) = x^2 - 2x - 3\) (not listed)
Thus II and III are factors.
Question 16
A cylinder of radius 5 cm is inside a cylinder of radius 10 cm. Both have height 20 cm. What is the volume between them?
Solution
Volume of larger cylinder: \(V_2 = \pi \times 10^2 \times 20 = 2000\pi\) cm³
Volume of smaller cylinder: \(V_1 = \pi \times 5^2 \times 20 = 500\pi\) cm³
Volume between: \(V = V_2 - V_1 = 2000\pi - 500\pi = 1500\pi\) cm³
Question 17
A data set has a standard deviation equal to 1. If each data value in the data set is multiplied by 4, then the value of the standard deviation of the new data set is equal to:
Solution
Multiplying each data value by \(k\) multiplies the standard deviation by \(|k|\).
Here \(k = 4\), old standard deviation = 1, so new standard deviation = \(4 \times 1 = 4\).
Question 18
A cone made of cardboard has a vertical height of 8 cm and a radius of 6 cm. If this cone is cut along the slanted height to make a sector, what is the central angle, in degrees, of the sector?

Solution
Base circumference: \(P = 2\pi r = 2\pi \times 6 = 12\pi\) cm
Slant height: \(H = \sqrt{r^2 + h^2} = \sqrt{6^2 + 8^2} = \sqrt{36 + 64} = \sqrt{100} = 10\) cm
Arc length of sector = base circumference: \(S = H \cdot \theta = 10\theta\)
Set equal: \(10\theta = 12\pi \Rightarrow \theta = \frac{12\pi}{10} = 1.2\pi\) radians
Convert to degrees: \(\theta = 1.2\pi \times \frac{180}{\pi} = 216^\circ\)
Question 19
If \(\sin(x) = -\frac{1}{3}\) and \(\pi \le x \le \frac{3\pi}{2}\), then \(\cot(2x) = ?\)
Solution
First find \(\cos(x)\) (x in QIII, so negative):
\(\cos(x) = -\sqrt{1 - \sin^2(x)} = -\sqrt{1 - \frac{1}{9}} = -\sqrt{\frac{8}{9}} = -\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}\)
Find \(\tan(x)\): \(\tan(x) = \frac{\sin(x)}{\cos(x)} = \frac{-\frac{1}{3}}{-\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}} = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
Use double-angle formula: \(\cot(2x) = \frac{1 - \tan^2(x)}{2\tan(x)}\)
\(\cot(2x) = \frac{1 - \frac{1}{8}}{2 \cdot \frac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}} = \frac{\frac{7}{8}}{\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}} = \frac{7}{8} \times \sqrt{2} = \frac{7\sqrt{2}}{8}\)
Question 20
Which of the following functions satisfy the condition \(f(x) = f^{-1}(x)\)?
I) \(f(x) = -x\)
II) \(f(x) = \sqrt{x}\)
III) \(f(x) = -\frac{1}{x}\)
Solution
For \(f(x) = -x\): inverse is \(f^{-1}(x) = -x\), so condition holds.
For \(f(x) = \sqrt{x}\): inverse is \(f^{-1}(x) = x^2\), so condition does NOT hold.
For \(f(x) = -\frac{1}{x}\): inverse is \(f^{-1}(x) = -\frac{1}{x}\), so condition holds.
Thus I and III satisfy.
Question 21
If \(f(x) = \frac{1}{x - 2}\), which of the following graphs is closest to the graph of \(|f(x)|\)?

Solution
\(|f(x)| = \left|\frac{1}{x-2}\right|\) is always nonnegative and undefined at \(x=2\).
Only graph C shows a vertical asymptote at \(x=2\) with all y-values ≥ 0.
Question 22
If in a triangle ABC, \(\sin(A) = \frac{1}{5}\), \(\cos(B) = \frac{2}{7}\), then \(\cos(C) = ?\)
Solution
Using angle sum: \(C = \pi - (A + B)\), so \(\cos(C) = -\cos(A + B)\)
Cosine addition formula: \(\cos(C) = -[\cos A \cos B - \sin A \sin B] = \sin A \sin B - \cos A \cos B\)
Find \(\cos A\): \(\cos A = \sqrt{1 - \sin^2 A} = \sqrt{1 - \frac{1}{25}} = \sqrt{\frac{24}{25}} = \frac{2\sqrt{6}}{5}\)
Find \(\sin B\): \(\sin B = \sqrt{1 - \cos^2 B} = \sqrt{1 - \frac{4}{49}} = \sqrt{\frac{45}{49}} = \frac{3\sqrt{5}}{7}\)
Substitute: \(\cos(C) = \left(\frac{1}{5}\right)\left(\frac{3\sqrt{5}}{7}\right) - \left(\frac{2\sqrt{6}}{5}\right)\left(\frac{2}{7}\right) = \frac{3\sqrt{5}}{35} - \frac{4\sqrt{6}}{35} = \frac{3\sqrt{5} - 4\sqrt{6}}{35}\)
Question 23
Find the sum: \(\displaystyle \sum_{k=1}^{100} (3 + k)\)
Solution
Write out terms: \(4 + 5 + 6 + \dots + 103\)
Arithmetic series with \(n=100\), \(a_1=4\), \(a_{100}=103\)
Sum: \(S = \frac{n(a_1 + a_n)}{2} = \frac{100(4 + 103)}{2} = 50 \times 107 = 5350\)
Question 24
What value of \(x\) makes the three terms \(x\), \(\frac{x}{x + 1}\), and \(\frac{3x}{(x + 1)(x + 2)}\) those of a geometric sequence?
Solution
For geometric sequence: \(\frac{\text{term}_2}{\text{term}_1} = \frac{\text{term}_3}{\text{term}_2}\)
\(\frac{\frac{x}{x+1}}{x} = \frac{\frac{3x}{(x+1)(x+2)}}{\frac{x}{x+1}}\)
Simplify left: \(\frac{1}{x+1}\)
Simplify right: \(\frac{3}{x+2}\)
Set equal: \(\frac{1}{x+1} = \frac{3}{x+2}\)
Cross-multiply: \(x + 2 = 3(x + 1)\)
\(x + 2 = 3x + 3\)
\(-2x = 1 \Rightarrow x = -\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 25
As \(x\) increases from \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) to \(\frac{3\pi}{4}\), \(|\sin(2x)|\):
A) always increases
B) always decreases
C) increases then decreases
D) decreases then increases
E) stay constant
Solution
Evaluate at key points:
\(x = \frac{\pi}{4}\): \(|\sin(\frac{\pi}{2})| = 1\)
\(x = \frac{\pi}{2}\): \(|\sin(\pi)| = 0\)
\(x = \frac{3\pi}{4}\): \(|\sin(\frac{3\pi}{2})| = 1\)
Pattern: decreases from 1 to 0, then increases from 0 to 1.
Answer: D) decreases then increases
Question 26
If \(ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d\) is divided by \(x - 2\), then the remainder is equal to:
Solution
By the Remainder Theorem, remainder = \(P(2) = a(2)^3 + b(2)^2 + c(2) + d\)
\(= 8a + 4b + 2c + d\)
Question 27
A committee of 6 teachers is to be formed from 5 male teachers and 8 female teachers. If selected at random, what is the probability that it has an equal number of male and female teachers?
Solution
Equal numbers ⇒ 3 males and 3 females
Number of ways to choose 3 males from 5: \(\binom{5}{3} = 10\)
Number of ways to choose 3 females from 8: \(\binom{8}{3} = 56\)
Total ways to choose 6 from 13: \(\binom{13}{6} = 1716\)
Probability: \(\frac{10 \times 56}{1716} = \frac{560}{1716} = \frac{140}{429}\)
Question 28
The range of the function \(f(x) = -|x - 2| - 3\) is:
Solution
Since \(|x - 2| \ge 0\): \(-|x - 2| \le 0\)
Then \(-|x - 2| - 3 \le -3\)
Thus \(f(x) \le -3\) for all \(x\)
Range: \((-\infty, -3]\)
Question 29
What is the period of the function \(f(x) = 3 \sin^2(2x + \frac{\pi}{4})\)?
Solution
Use power-reduction identity: \(\sin^2 \theta = \frac{1 - \cos 2\theta}{2}\)
\(f(x) = 3 \cdot \frac{1 - \cos(4x + \frac{\pi}{2})}{2} = \frac{3}{2} - \frac{3}{2} \cos(4x + \frac{\pi}{2})\)
Period of \(\cos(Bx + C)\) is \(\frac{2\pi}{|B|}\)
Here \(B = 4\), so period = \(\frac{2\pi}{4} = \frac{\pi}{2}\)
Question 30
It is known that 3 out of 10 television sets are defective. If 2 television sets are selected at random from the 10, what is the probability that 1 of them is defective?
Solution
Number of ways to choose 1 defective from 3: \(\binom{3}{1} = 3\)
Number of ways to choose 1 non-defective from 7: \(\binom{7}{1} = 7\)
Total ways to choose 2 from 10: \(\binom{10}{2} = 45\)
Probability: \(\frac{3 \times 7}{45} = \frac{21}{45} = \frac{7}{15}\)
Question 31
In a triangle ABC, angle B has a size of 50°, angle A has a size of 32° and the length of side BC is 150 units. The length of side AB is:
Solution
Find angle C: \(C = 180^\circ - (50^\circ + 32^\circ) = 98^\circ\)
Use Law of Sines: \(\frac{AB}{\sin C} = \frac{BC}{\sin A}\)
\(AB = \frac{BC \cdot \sin C}{\sin A} = \frac{150 \cdot \sin 98^\circ}{\sin 32^\circ}\)
Approximate: \(\sin 98^\circ \approx 0.9903\), \(\sin 32^\circ \approx 0.5299\)
\(AB \approx \frac{150 \times 0.9903}{0.5299} \approx 280\) units
Question 32
For the remainder of the division of \(x^3 - 2x^2 + 3kx + 18\) by \(x - 6\) to be equal to zero, \(k\) must be equal to:
Solution
By Remainder Theorem, remainder = \(P(6)\)
\(P(6) = 6^3 - 2(6)^2 + 3k(6) + 18 = 216 - 72 + 18k + 18 = 162 + 18k\)
Set remainder = 0: \(162 + 18k = 0\)
\(18k = -162 \Rightarrow k = -9\)
Question 33
It takes pump A 4 hours to empty a swimming pool. It takes pump B 6 hours to empty the same swimming pool. If the two pumps are started together, at what time will the two pumps have emptied 50% of the water in the swimming pool?
Solution
Pump A rate: \(\frac{1}{4}\) pool/hour
Pump B rate: \(\frac{1}{6}\) pool/hour
Combined rate: \(\frac{1}{4} + \frac{1}{6} = \frac{5}{12}\) pool/hour
Time to empty 50% = 0.5 pool: \(t \times \frac{5}{12} = 0.5\)
\(t = 0.5 \times \frac{12}{5} = 1.2\) hours = 1 hour 12 minutes
Question 34
The graph of \(r = 10 \cos \theta\), where \(r\) and \(\theta\) are polar coordinates, is:
A) a circle
B) an ellipse
C) a horizontal line
D) a hyperbola
E) a vertical line
Solution
Convert to rectangular: \(r = 10\cos \theta\)
Multiply by \(r\): \(r^2 = 10r\cos \theta\)
Substitute \(r^2 = x^2 + y^2\), \(r\cos \theta = x\): \(x^2 + y^2 = 10x\)
Rearrange: \(x^2 - 10x + y^2 = 0\)
Complete square: \((x - 5)^2 + y^2 = 25\)
This is a circle with center (5,0) and radius 5.
Answer: A) a circle
Question 35
If \((2 - i)(a - bi) = 2 + 9i\), where \(i\) is the imaginary unit and \(a\) and \(b\) are real numbers, then \(a\) equals:
Solution
Expand left side: \((2 - i)(a - bi) = 2a - 2bi - ai + bi^2\)
Since \(i^2 = -1\): \(= 2a - 2bi - ai - b = (2a - b) + (-2b - a)i\)
Set equal to \(2 + 9i\): \(2a - b = 2\) and \(-2b - a = 9\)
Solve system: From first equation, \(b = 2a - 2\)
Substitute into second: \(-2(2a - 2) - a = 9\)
\(-4a + 4 - a = 9\)
\(-5a = 5 \Rightarrow a = -1\)
Question 36
Lines L1 and L2 are perpendicular and intersect at the point \((2, 3)\). If L1 passes through the point \((0, 2)\), then line L2 must pass through the point:
A) \((0, 3)\)
B) \((1, 1)\)
C) \((3, 1)\)
D) \((5, 0)\)
E) \((6, 7)\)
Solution
Slope of L1 through \((2,3)\) and \((0,2)\): \(m_1 = \frac{3 - 2}{2 - 0} = \frac{1}{2}\)
Since L1 ⟂ L2, slope of L2: \(m_2 = -\frac{1}{m_1} = -2\)
Equation of L2 through \((2,3)\): \(y - 3 = -2(x - 2) \Rightarrow y = -2x + 7\)
Check which point satisfies:
A) \((0,3)\): \(3 = -2(0) + 7?\) No
B) \((1,1)\): \(1 = -2(1) + 7?\) No
C) \((3,1)\): \(1 = -2(3) + 7?\) Yes
D) \((5,0)\): \(0 = -2(5) + 7?\) No
E) \((6,7)\): \(7 = -2(6) + 7?\) No
Answer: C) \((3, 1)\)
Question 37
A square pyramid is inscribed in a cube of total surface area of 24 square cm such that the base of the pyramid is the same as the base of the cube. What is the volume of the pyramid?
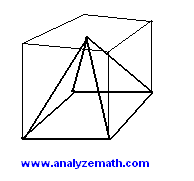
Solution
Cube has 6 faces, total area 24 cm²: area of one face = \(\frac{24}{6} = 4\) cm²
Side length of cube face: \(s = \sqrt{4} = 2\) cm
Pyramid base = cube base, height = cube side: base area = 4 cm², height = 2 cm
Volume of pyramid: \(V = \frac{1}{3} \times \text{base area} \times \text{height} = \frac{1}{3} \times 4 \times 2 = \frac{8}{3}\) cm³
Question 38
The graph defined by the parametric equations \(x = \cos^2 t\), \(y = 3 \sin t - 1\) is:
Solution
From \(y = 3\sin t - 1\): \(\sin t = \frac{y + 1}{3}\)
Square: \(\sin^2 t = \frac{(y + 1)^2}{9}\)
Use identity \(\cos^2 t = 1 - \sin^2 t\): \(x = 1 - \frac{(y + 1)^2}{9}\)
Rearrange: \(\frac{(y + 1)^2}{9} = 1 - x\)
\((y + 1)^2 = 9(1 - x)\)
This is a parabola opening left. Restrictions: since \(x = \cos^2 t\), \(0 \le x \le 1\); since \(y = 3\sin t - 1\), \(-4 \le y \le 2\)
Thus the graph is a portion of a parabola.
Question 39
\(\displaystyle \lim_{x \to 2} \frac{x^4 - 16}{x - 2} = ?\)

Solution
Factor numerator: \(x^4 - 16 = (x^2 - 4)(x^2 + 4) = (x - 2)(x + 2)(x^2 + 4)\)
Simplify: \(\frac{x^4 - 16}{x - 2} = \frac{(x - 2)(x + 2)(x^2 + 4)}{x - 2} = (x + 2)(x^2 + 4)\) for \(x \ne 2\)
Take limit: \(\lim_{x \to 2} (x + 2)(x^2 + 4) = (4)(4 + 4) = 4 \times 8 = 32\)
Question 40
For \(x > 0\) and \(x \ne 1\), \(\log_{16}(x) = ?\)
Solution
Use change of base formula: \(\log_{16}(x) = \frac{\log_2(x)}{\log_2(16)}\)
Since \(16 = 2^4\): \(\log_2(16) = 4\)
Thus: \(\log_{16}(x) = \frac{\log_2(x)}{4} = 0.25 \log_2(x)\)
Question 41
The value of \(k\) that makes function \(f\), defined below, continuous is:
\(f(x) = \begin{cases}
\frac{2x^2 + 5x}{x} & \text{if } x \ne 0 \\
3k - 1 & \text{if } x = 0
\end{cases}\)

Solution
Simplify for \(x \ne 0\): \(\frac{2x^2 + 5x}{x} = 2x + 5\)
Limit as \(x \to 0\): \(\lim_{x \to 0} f(x) = \lim_{x \to 0} (2x + 5) = 5\)
For continuity at \(x=0\): \(f(0) = \lim_{x \to 0} f(x)\)
\(3k - 1 = 5\)
\(3k = 6 \Rightarrow k = 2\)
Question 42
If \(\log_b(a) = x\) and \(\log_b(c) = y\), and \(4x + 6y = 8\), then \(\log_b(a^2 \cdot c^3) = ?\)
Solution
Given: \(4x + 6y = 8\)
Divide by 2: \(2x + 3y = 4\)
Substitute \(x = \log_b(a)\), \(y = \log_b(c)\): \(2\log_b(a) + 3\log_b(c) = 4\)
Use logarithm properties: \(\log_b(a^2) + \log_b(c^3) = 4\)
\(\log_b(a^2 \cdot c^3) = 4\)
Question 43
The point \((0, -2, 5)\) lies on the:
Solution
The x-coordinate is 0, so the point lies on the yz-plane.
Question 44
Curve C is defined by the equation \(y = \sqrt{9 - x^2}\) with \(x \ge 0\). The area bounded by curve C, the x-axis and the y-axis is:
Solution
Equation represents a quarter circle: \(x^2 + y^2 = 9\) with \(x \ge 0, y \ge 0\)
Radius \(r = 3\), area of full circle = \(\pi r^2 = 9\pi\)
Area of quarter circle: \(\frac{1}{4} \times 9\pi = \frac{9\pi}{4}\)
Question 45
In a plane there are 6 points such that no three points are collinear. How many triangles do these points determine?
Solution
A triangle is determined by 3 non-collinear points.
Number of triangles = \(\binom{6}{3} = \frac{6 \times 5 \times 4}{3 \times 2 \times 1} = 20\)
Question 46
Find \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) given the matrix multiplication:
\(\begin{pmatrix} 3 & 2 \\ -1 & -2 \end{pmatrix}
\begin{pmatrix} 0 & a \\ b & c \end{pmatrix}
= \begin{pmatrix} -4 & 9 \\ 0 & -7 \end{pmatrix}\)
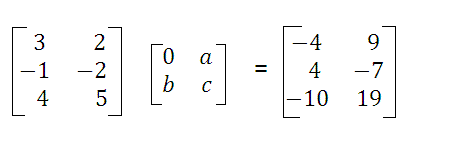
Solution
From first row × first column: \(3(0) + 2b = -4 \Rightarrow 2b = -4 \Rightarrow b = -2\)
From first row × second column: \(3a + 2c = 9\) ... (1)
From second row × second column: \((-1)a + (-2)c = -7 \Rightarrow -a - 2c = -7\) ... (2)
Multiply (2) by 2: \(-2a - 4c = -14\)
Add to (1): \((3a + 2c) + (-2a - 4c) = 9 + (-14) \Rightarrow a - 2c = -5\) ... (3)
From (2): \(a = 7 - 2c\)
Substitute into (3): \((7 - 2c) - 2c = -5 \Rightarrow 7 - 4c = -5\)
\(-4c = -12 \Rightarrow c = 3\)
Then \(a = 7 - 2(3) = 1\)
Thus \(a = 1, b = -2, c = 3\)
Question 47
If the sum of the repeating decimals \(0.353535... + 0.252525...\) is written as a fraction in lowest terms, the product of the numerator and denominator is:
Solution
Express as fractions:
\(0.\overline{35} = \frac{35}{99}\)
\(0.\overline{25} = \frac{25}{99}\)
Sum: \(\frac{35}{99} + \frac{25}{99} = \frac{60}{99} = \frac{20}{33}\)
Product of numerator and denominator: \(20 \times 33 = 660\)
Question 48
\(\sin(\tan^{-1} \sqrt{2}) = ?\)
Solution
Let \(\theta = \tan^{-1} \sqrt{2}\), so \(\tan \theta = \sqrt{2} = \frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{adjacent}} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{1}\)
Construct right triangle: opposite = \(\sqrt{2}\), adjacent = 1
Hypotenuse = \(\sqrt{(\sqrt{2})^2 + 1^2} = \sqrt{2 + 1} = \sqrt{3}\)
\(\sin \theta = \frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{hypotenuse}} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}} = \sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\)
Question 49
If \(8^x = 2\) and \(3^{x+y} = 81\), then \(y = ?\)
Solution
Solve \(8^x = 2\): \((2^3)^x = 2^1 \Rightarrow 2^{3x} = 2^1 \Rightarrow 3x = 1 \Rightarrow x = \frac{1}{3}\)
Solve \(3^{x+y} = 81\): \(3^{x+y} = 3^4 \Rightarrow x + y = 4\)
Substitute \(x = \frac{1}{3}\): \(\frac{1}{3} + y = 4 \Rightarrow y = 4 - \frac{1}{3} = \frac{11}{3}\)
Question 50
Let \(f(x) = -\frac{x^2}{2}\). If the graph of \(f(x)\) is translated 2 units up and 3 units left and the resulting graph is that of \(g(x)\), then \(g(\frac{1}{2}) = ?\)
Solution
Start with \(f(x) = -\frac{x^2}{2}\)
Translate 2 units up: \(-\frac{x^2}{2} + 2\)
Translate 3 units left (replace \(x\) with \(x+3\)): \(g(x) = -\frac{(x+3)^2}{2} + 2\)
Evaluate at \(x = \frac{1}{2}\): \(g(\frac{1}{2}) = -\frac{(\frac{1}{2}+3)^2}{2} + 2 = -\frac{(\frac{7}{2})^2}{2} + 2\)
\(= -\frac{\frac{49}{4}}{2} + 2 = -\frac{49}{8} + 2 = -\frac{49}{8} + \frac{16}{8} = -\frac{33}{8}\)