Find The Area of a Circle Using Integrals in Calculus
Find the area of a circle of radius \( a \) using integrals in calculus.
Problem : Find the area of a circle with radius \( a \).

Solution to the problem:
The equation of the circle shown above is given by
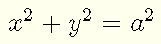
The circle is symmetric with respect to the x and y axes, hence we can find the area of one quarter of a circle and multiply by 4 in order to obtain the total area of the circle.
Solve the above equation for \( y \)
\[ y = \pm \sqrt{ a^2 - x^2 } \]
The equation of the upper semi circle (y positive) is given by
\[ y = \sqrt { a^2 - x^2 } \]
Factor out \( a^2 \) inside the radicand
\[ y = \sqrt { a^2(1 - x^2/a^2) } \]
Take \( a^2 \) from under the radicand and rewrite \( y \) as follows
\[ y = a \sqrt { 1 - x^2 / a^2 } \]
We use integrals to find the area of the upper right quarter of the circle as follows
 \[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = \int_0^a a \sqrt{1-x^2/a^2} dx \]
Let us substitute \( \; x / a \) by \( \; \sin t \) so that \( \sin t = x / a \) and \( dx = a \cos t \; dt \; \) and the area is given by
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = \int_0^{\pi/2} a^2 \sqrt{1-\sin^2t} \cos t \; dt\]
We now use the trigonometric identity
\[ \sin^2 t + \cos^2 t = 1 \]
which gives
\[ \sqrt{1-\sin^2t} = \cos t \quad \] since t varies from \( 0 \) to \( \pi/2 \)
hence
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = \int_0^{\pi/2} a^2 \cos^2t \; dt\]
Use the trigonometric identity \( \; \cos^2 t = ( \cos 2t + 1 ) / 2 \;\) to linearize the integrand;
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = \int_0^{\pi/2} a^2 ( \cos 2t + 1 ) / 2 \; dt\]
Evaluate the integral
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = (1/2)a^2 \left[(1/2) \sin 2t + t\right]_0^{\pi/2} \]
Simplify
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = (1/4) \pi a^2 \]
The total area of the circle is obtained by a multiplication by 4 of the above area.
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = 4 \times (1/4) \pi a^2 = \pi a^2 \]
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = \int_0^a a \sqrt{1-x^2/a^2} dx \]
Let us substitute \( \; x / a \) by \( \; \sin t \) so that \( \sin t = x / a \) and \( dx = a \cos t \; dt \; \) and the area is given by
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = \int_0^{\pi/2} a^2 \sqrt{1-\sin^2t} \cos t \; dt\]
We now use the trigonometric identity
\[ \sin^2 t + \cos^2 t = 1 \]
which gives
\[ \sqrt{1-\sin^2t} = \cos t \quad \] since t varies from \( 0 \) to \( \pi/2 \)
hence
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = \int_0^{\pi/2} a^2 \cos^2t \; dt\]
Use the trigonometric identity \( \; \cos^2 t = ( \cos 2t + 1 ) / 2 \;\) to linearize the integrand;
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = \int_0^{\pi/2} a^2 ( \cos 2t + 1 ) / 2 \; dt\]
Evaluate the integral
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = (1/2)a^2 \left[(1/2) \sin 2t + t\right]_0^{\pi/2} \]
Simplify
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = (1/4) \pi a^2 \]
The total area of the circle is obtained by a multiplication by 4 of the above area.
\[ \dfrac{1}{4} \text{Area of circle} = 4 \times (1/4) \pi a^2 = \pi a^2 \]
References


