Geometry Problems with Solutions and Answers
Grade 11 geometry problems with detailed solutions are presented.
Question 1
Find all points of intersection of the circle \( x^2 + 2x + y^2 + 4y = -1 \) and the line \( x - y = 1 \).
Solve the linear equation \( x - y = 1 \) for \( x \):
\( x = 1 + y \)
Substitute into the standard equation of the given circle :
\[ (1 + y)^2 + 2(1 + y) + y^2 + 4y = -1 \]
Expand and simplify the expression. Combine like terms and rewrite the resulting quadratic equation in standard form:
\[ 2y^2 + 8y + 4 = 0 \]
Solve the quadratic equation to get the values of \( y \):
\[ y = -2 \pm \sqrt{2} \]
Use the substitution \( x = 1 + y \) to find the corresponding \( x \)-values.
Therefore, the points of intersection between the line and the circle are:
\[ (-1 + \sqrt{2},\ -2 + \sqrt{2}) \quad \text{and} \quad (-1 - \sqrt{2},\ -2 - \sqrt{2}) \]
Question 2
Find the area of the triangle enclosed by the x - axis and the lines y = x and y = -2x + 3.
To find the area of the triangle formed by the lines \( y = x \) and \( y = -2x + 3 \), first graph both lines.

Solve the system of equations to find the intersection point:
\[ y = x \quad \text{and} \quad \; y = -2x + 3 \]
Solving, we find the intersection point is \( (1,\ 1) \). The height of the triangle is 1 (the y-coordinate).
The x-intercept of \( y = -2x + 3 \) is found by setting \( y = 0 \): \[ 0 = -2x + 3 \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{3}{2} \]
The base of the triangle is \( \dfrac{3}{2} \). So, the area is:
\[ \text{Area} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{3}{2} \times 1 = \dfrac{3}{4} \]
Question 3
Find the length of the third side of a triangle if the area of the triangle is 18 and two of its sides have lengths of 5 and 10.
The sine formula for the area of a triangle using two sides and the included angle can be written as:
\[ 18 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 5 \times 10 \times \sin(A) \]Solving for \( \sin(A) \), we get:
\[ \sin(A) = \dfrac{18}{25} \]We now use the cosine law to find the length \( x \) of the third side opposite angle \( A \):
\[ x^2 = 5^2 + 10^2 - 2 \times 5 \times 10 \times \cos(A) \]Since \( \cos(A) = \sqrt{1 - \sin^2(A)} \), we substitute:
\[ \cos(A) = \sqrt{1 - \left(\dfrac{18}{25}\right)^2} \]Substitute \( \cos(A) \) into the cosine law expression and solve for \( x \):
\[ x \approx 7.46 \quad \text{(rounded to 3 significant digits)} \]Question 4
In the figure below points A, B, C and D are on a circle. Point O is the intersection of chords AC and BD. The area of triangle BOC is 15; the length of AO is 10 and the length of OB is 5. What is the area of triangle AOD?
 .
.
The area of triangle BOC is 15 and is given by \[ \text{Area}_{\triangle BOC} = \dfrac{1}{2} \cdot BO \cdot OC \cdot \sin(\angle BOC) \]
The area of triangle AOD is given by \[ \text{Area}_{\triangle AOD} = \dfrac{1}{2} \cdot AO \cdot OD \cdot \sin(\angle AOD) \]
Note that angles \( \angle BOC \) and \( \angle AOD \) are equal.
By the theorem of the intersecting chords, we have: \[ AO \cdot OC = BO \cdot OD \]
This can be written as: \[ \dfrac{AO}{BO} = \dfrac{OD}{OC} = \dfrac{10}{5} = 2 \]
The ratios \( \dfrac{AO}{BO} \) and \( \dfrac{OD}{OC} \) are both equal to 2, hence their product is: \[ \dfrac{AO \cdot OD}{BO \cdot OC} = 4 \]
Which gives: \[ AO \cdot OD = 4 \cdot (BO \cdot OC) \]
Therefore, the area of triangle AOD is 4 times the area of triangle BOC: \[ \text{Area}_{\triangle AOD} = 4 \cdot 15 = 60 \]

Question 5
The two circles below are concentric (have same center). The radius of the large circle is 10 and that of the small circle is 6. What is the length of the chord AB?
 .
.
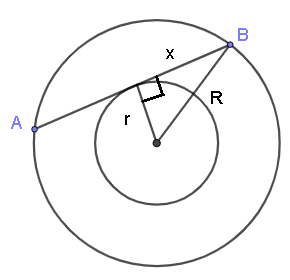
If we draw a radius in the small circle to the point of tangency, it will be at right angle with the chord (see figure below). If \( x \) is half the length of \( AB \), \( r \) is the radius of the small circle, and \( R \) is the radius of the large circle, then by the Pythagorean Theorem, we have:
\[ r^2 + x^2 = R^2 \] \[ 6^2 + x^2 = 10^2 \]Solve for \( x \): \( x = 8 \)
Length of \( AB = 2x = 16 \)
Question 6
Point A is inside the square BCDE whose side length is 20. The length of AB is 9 and the length of AE is 13. Find x the length of AC.
 .
.
Use cosine law in triangle ABE:
\[ 13^2 = 20^2 + 9^2 - 2(20)(9)\cos(T) \tag{I} \]Use cosine law in triangle ACB:
\[ x^2 = 20^2 + 9^2 - 2(20)(9)\cos(90^\circ - T) \]

Note that \( \cos(90^\circ - T) = \sin(T) \) and rewrite the second equation as:
\[ x^2 = 20^2 + 9^2 - 2(20)(9)\sin(T) \tag{III} \]Solve equation (I) for \( \cos(T) \):
\[ \cos(T) = \dfrac{13}{15} \]Use the trigonometric identity \( \sin(T) = \sqrt{1 - \cos^2(T)} \) to find:
\[ \sin(T) = \dfrac{2\sqrt{14}}{15} \]Substitute \( \sin(T) = \dfrac{2\sqrt{14}}{15} \) into equation (III) and solve for \( x \):
\[ x = \sqrt{481 - 48\sqrt{14}} \approx 17.4 \](Approximated to 3 significant digits.)
Question 7
A metal object is made by joining a hemisphere to the top of a right circular cylinder.
The radius of both the hemisphere and the cylinder is \( r = 5 \, \text{cm} \).
The height of the cylinder is \( h = 12 \, \text{cm} \).
a) Calculate the total volume of the object in terms of \( \pi\).
b) If the metal has a density of \( 7.8 \, \text{g/cm}^3$ \) , calculate the mass of the object.
a) Volume of the Composite Solid 1. Volume of the cylinder: \[ V_{\text{cylinder}} = \pi r^2 h = \pi (5)^2 (12) = \pi (25)(12) = 300\pi \, \text{cm}^3 \] 2. Volume of the hemisphere: \[ V_{\text{hemisphere}} = \frac{1}{2} \left( \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3 \right) = \frac{2}{3} \pi (5)^3 = \frac{2}{3} \pi (125) = \frac{250}{3} \pi \, \text{cm}^3 \] 3. Total volume: \[ V_{\text{total}} = V_{\text{cylinder}} + V_{\text{hemisphere}} = 300\pi + \frac{250}{3}\pi = \left( \frac{900 + 250}{3} \right)\pi = \frac{1150}{3} \pi \, \text{cm}^3 \] b) Mass of the Object \[ \text{Mass} = \text{Density} \times \text{Volume} = 7.8 \times \frac{1150}{3} \pi \] Approximating using \(\pi \approx 3.1416 \): \[ \text{Mass} \approx 7.8 \times \frac{1150}{3} \times 3.1416 \approx 9396.66 \, \text{g} \]
Question 8
A garden is shaped like a rectangle with a semicircle attached to one of the shorter sides.
The rectangle is 12 meters long and 8 meters wide.
The semicircle is attached along the 8-meter side.
a) Calculate the total area of the garden.
b) Calculate the perimeter of the garden (excluding the boundary where the semicircle meets the rectangle).
a) Area of the Garden 1. Area of the rectangle: \[ A_{\text{rect}} = \text{length} \times \text{width} = 12 \times 8 = 96 \, \text{m}^2 \] 2. **Area of the semicircle (with radius $r = 4$ meters): \[ A_{\text{semi}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi (4)^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi (16) = 8\pi \, \text{m}^2 \] 3. **Total area: \[ A_{\text{total}} = A_{\text{rect}} + A_{\text{semi}} = 96 + 8\pi \, \text{m}^2 \] Using $\pi \approx 3.1416$: \[ A_{\text{total}} \approx 96 + 8(3.1416) = 96 + 25.13 = \boxed{121.13 \, \text{m}^2} \] b) Perimeter of the Garden Note: We exclude the shared edge between the semicircle and rectangle. 1. Three sides of the rectangle (excluding the 8 m side): \[ P_{\text{rect}} = 12 + 8 + 12 = 32 \, \text{m} \] 2. Curved part of the semicircle: \[ P_{\text{semi}} = \frac{1}{2} (2\pi r) = \pi r = \pi \cdot 4 = 4\pi \, \text{m} \] 3. Total perimeter: \[ P_{\text{total}} = 32 + 4\pi \approx 32 + 12.566 = \boxed{44.57 \, \text{m}} \]
More References and Links
- Intersecting Chords Theorem Questions with Solutions
- Equation of a Circle
- Solve Quadratic Equations Using Discriminants
- Area of Triangle Using Sine Formula
- Pythagorean Theorem and Problems with Solutions
- Cosine Law Problems
- High School Math (Grades 10, 11 and 12) - Free Questions and Problems With Answers
- Middle School Math (Grades 6, 7, 8, 9) - Free Questions and Problems With Answers
- Primary Math (Grades 4 and 5) with Free Questions and Problems With Answers
- Home Page