This tutorial explains how to graph piecewise functions step by step. We examine their graphs, domains, ranges, and key properties. You may also use free graph paper to sketch the graphs by hand.
A piecewise function is a function defined by different formulas on different intervals of its domain.
The domain of this function is all real numbers since a formula is defined for every value of \(x\).
This is a piecewise constant function. The domain is all real numbers except \(x = -3\).
Using the definition of absolute value:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} x, & x \ge 0 \\ -x, & x < 0 \end{cases} \]The domain is all real numbers.
This function is defined for all real numbers.
The function is undefined on the interval \((-2, 2]\) and at \(x = 4\).
The domain is all real numbers. The range is: \[ \{-1,\, 2\} \]
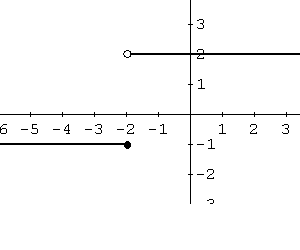
The domain is all real numbers, and the range is: \[ (-\infty, +\infty) \]
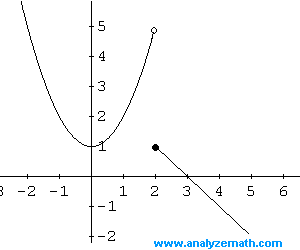
The horizontal asymptote is \(y = 0\).
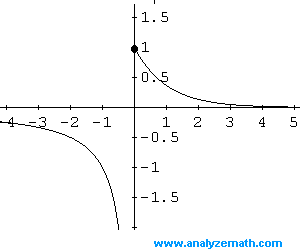
The domain is all real numbers and the range is: \[ \{-1\} \cup [1, +\infty) \]
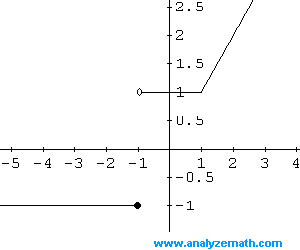
More references: Graphing Functions