Right Triangle Problems with Step-by-Step Solutions
This page presents solved right triangle problems using the Pythagorean theorem and trigonometric ratios.
Each example includes clear explanations and mathematical reasoning.
Example 1
Find \( \sin(x) \) and \( \cos(x) \) in the right triangle shown below.

Solution
Use the
Pythagorean theorem
to find the hypotenuse \( h \):
\[
h = \sqrt{6^2 + 8^2} = \sqrt{36 + 64} = 10
\]
Using trigonometric ratios:
\[
\sin(x) = \frac{8}{10} = 0.8
\]
And
\[
\cos(x) = \frac{6}{10} = 0.6
\]
Example 2
Two lines tangent to a circle at points \(M\) and \(N\) intersect at point \(A\).
The angle \( \angle MAN = x^\circ \) and the circle has radius \(r\).
Find the distance from \(A\) to the center of the circle.

Solution
The radius is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact, forming right angles at \(M\) and \(N\).
Triangles \(MAC\) and \(NAC\) are congruent right triangles. Using tangent:
\[
\tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \frac{r}{NA}
\]
Solving for \(NA\):
\[
NA = \frac{r}{\tan(x/2)}
\]
Apply the Pythagorean theorem in triangle \(NAC\):
\[
AC = \sqrt{r^2 + NA^2}
\]
Substitute:
\[
AC = \sqrt{r^2 + \left(\frac{r}{\tan(x/2)}\right)^2}
\]
Factor and simplify:
\[
AC = r \sqrt{1 + \frac{1}{\tan^2(x/2)}}
\]
Example 3
Two right triangles share a common side \(a\).
Find \( \tan(x) \).

Solution
From the right triangle on the right:
\[
\tan(41^\circ) = \frac{a}{15}
\]
Solve for \(a\):
\[
a = 15 \tan(41^\circ)
\]
From the left triangle:
\[
\tan(x) = \frac{a}{10}
\]
Substitute:
\[
\tan(x) = \frac{15 \tan(41^\circ)}{10}
\]
Final result:
\[
\tan(x) = 1.5 \tan(41^\circ)
\]
Example 4
An observer measures the angle of elevation of a tower from two points \(A\) and \(B\).
The distance between the points is \(d\).
Find the height \(h\) of the tower.

Solution
From triangle \(ACD\):
\[
\tan(a) = \frac{h}{d + x}
\]
From triangle \(BCD\):
\[
\tan(b) = \frac{h}{x}
\]
Solve for \(x\):
\[
x = \frac{h}{\tan(b)}
\]
Substitute into the first equation and solve for \(h\):
\[
h = \frac{d \tan(a) \tan(b)}{\tan(b) - \tan(a)}
\]
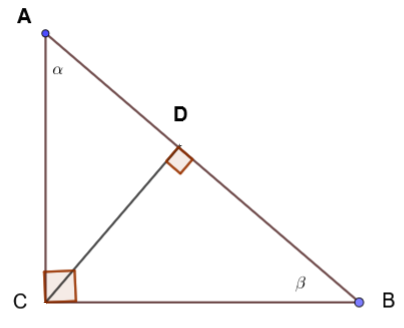
Example 5 - Challenging Problem
In a right triangle \(ABC\), the right angle is at point \(C\).
Let point \(D\) lie on the hypotenuse \(AB\) such that
\[
CD \perp AB.
\]
The angles at points \(A\) and \(B\) are denoted by \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \),
respectively.
Show that
\[
\tan(\alpha) + \tan(\beta) = \frac{AB}{CD}.
\]
Solution
Since \(CD\) is perpendicular to the hypotenuse \(AB\),
triangles \(ACD\) and \(BCD\) are right triangles.
In right triangle \(ACD\), we write:
\[
\tan(\alpha) = \frac{CD}{AD}.
\]
In right triangle \(BCD\), we write:
\[
\tan(\beta) = \frac{CD}{BD}.
\]
Add the two equations:
\[
\tan(\alpha) + \tan(\beta)
= CD\left(\frac{1}{AD} + \frac{1}{BD}\right).
\]
Combine the fractions:
\[
\tan(\alpha) + \tan(\beta)
= CD \cdot \frac{AD + BD}{AD \cdot BD}.
\]
Since point \(D\) lies on the hypotenuse \(AB\), we have:
\[
AD + BD = AB.
\]
Using the altitude-to-the-hypotenuse property of right triangles:
\[
CD^2 = AD \cdot BD.
\]
Substitute into the expression:
\[
\tan(\alpha) + \tan(\beta)
= CD \cdot \frac{AB}{CD^2}
= \frac{AB}{CD}.
\]
More References




