Grade 8 Problems on Circles and Solutions
Circle problems , for grade 8, are presented along with their detailed solutions. These problems deal with calculating circumference and area of circles.
Question 1
The three circles \( C_1 , \; C_2 \) and \( C_3 \) have their centers \( O_1 , \; O_2 \) and \(O_3 \) on the line \( L \) and are all tangent at the same point. If the diameter of the largest circle is \( 20 \) units, what is the ratio of the area of the largest circle to the area of the smallest circle?

The diameter of circle \( C_1 \) is equal to 20 units, so its radius is 10 units. The area \( A \) of the largest circle \( C_1 \) is: \[ A = \pi (10)^2 \] The diameter of circle \( C_2 \) is equal to the radius of circle \( C_1 \), which is 10 units. The diameter of circle \( C_3 \) is equal to the radius of circle \( C_2 \), which is 5 units. Therefore, the radius of circle \( C_3 \) is 2.5 units. We now calculate the area \( B \) of the smallest circle \( C_3 \): \[ B = \pi (2.5)^2 \] The ratio of \( A \) to \( B \) is given by: \[ \dfrac{A}{B} = \dfrac{\pi (10)^2}{\pi (2.5)^2} \] Simplifying: \[ = \dfrac{(10)^2}{(2.5)^2} = \left(\dfrac{10}{2.5}\right)^2 = 4^2 = 16 \]
Question 2
Mrs Parkinson's garden is made up of 4 squares and 2 semicircles as shown below. Each small square has an area of 4 square meters. Find the total area of the garden.
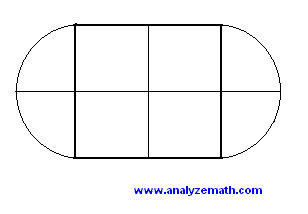
The garden is made up of 4 squares and 2 semicircles. The total area of the 4 squares is: \[ 4 \times 4 = 16 \text{ square meters} \] Since the area of one small square is 4 square meters, the side length \( s \) of each square is related to its area by: \[ s^2 = 4 \] Hence \[ s = \sqrt{4} = 2 \text{ meters} \] The radius of each semicircle is equal to the side of the square, so the radius is \( 2 \) meters. The two semicircles together form a complete circle. The area of the circle is: \[ \pi \times 2^2 = 4\pi \] So, the total area of the garden is: \[ 16 + 4\pi \approx 16 + 12.56 = 28.56 \text{ square meters} \quad (\text{using } \pi \approx 3.14) \]
Question 3
A water sprinkler can spray water at a maximum distance of \( 12 \) m in all directions. What area of the garden can this sprinkler irrigate? Round your answer to the nearest square meter.
One full rotation of the sprinkler would irrigate an area enclosed by a circle of radius 12 m. Hence, the area of the garden that the sprinkler can irrigate is given by the formula: \[ A = \pi r^2 = \pi (12)^2 = 144\pi \approx 452 \text{ square meters} \]
Question 4
A circular garden with a radius of \( 10 \) meters is surrounded by a walkway of width \( 1 \) meter. Find the area of the walkway (shaded part).

The walkway is enclosed between a smaller circle of radius \( 10 \) meters and a larger circle of radius \( 10+1 = 11 \) meters. Therefore, the area of the walkway is equal to the area enclosed by the larger circle minus the area enclosed by the smaller circle. \[ \text{Area of walkway} = \pi \times 11^2 - \pi \times 10^2 = 121\pi - 100\pi = 21\pi \text{ square meters.} \]
Question 5
A circular pizza costs \$19.99. What is the cost of 1 square centimeter if the diameter of the pizza is 36 cm?
The \$19.99 is the total cost of the whole pizza, whose area is: \[ \pi \times \left(\dfrac{36}{2}\right)^2 = 1017.87 \, \text{square cm} \] The cost of 1 square cm is equal to: \[ \dfrac{19.99}{1017.87} \approx 0.02 \, \text{dollars} = 2 \, \text{cents per square cm} \]
Question 6
How much fencing is needed for the Robinsons' circular flower garden that has an area of 5 square meters? (Round your answer to the nearest meter.)
The fencing will be put around the circular garden, and therefore the length of the fencing is equal to its circumference of the garden. The radius \( r \) of the garden is found using the area formula: \[ \pi \times r^2 = 5 \] Solving for \( r^2 \): \[ r^2 = \dfrac{5}{\pi} \] Taking the square root of both sides: \[ r = \sqrt{\dfrac{5}{\pi}} \approx 1.26 \text{ meters} \] The circumference of the garden is: \[ 2r \times \pi = 2 \times 1.26 \times \pi \approx 8 \text{ meters} \quad (\text{rounded to the nearest meter}) \] The length of the fencing needed is 8 meters.
Question 7
The radius of a circular disk is increased by 20%. What is the percent increase in the area of the disk?
If \( r \) is the radius of the disk, its area (before the increase) is given by: \[ A_{\text{before}} = \pi r^2 \] If the radius is increased by 20%, the new radius becomes: \[ r_{\text{new}} = r + 20\% \, r = r + \dfrac{20}{100} r = 1.2 r \] The area (after the increase) of the disk becomes: \[ A_{\text{after}} = \pi (1.2r)^2 = 1.44 \pi r^2 \] The change in area is: \[ \text{Change in area} = A_{\text{after}} - A_{\text{before}} = 1.44 \pi r^2 - \pi r^2 \] \[ = \pi r^2 (1.44 - 1) = 0.44 \pi r^2 \] The percent change in area is: \[ \text{Percent change in area} = \left( \dfrac{\text{Change}}{A_{\text{before}}} \right) \times 100\% = \left( \dfrac{0.44 \pi r^2}{\pi r^2} \right) \times 100\% \] \[ = 0.44 \times 100\% = 44\% \]
Question 8
A circular table has a diameter of 100 inches. A circular tablecloth hangs over the table 15 inches around the table. What is the area of the tablecloth?
If the table has a diameter of 100 inches and the tablecloth hangs 15 inches around the table, then the diameter of the tablecloth is equal to: \[ 100 + 15 + 15 = 130 \text{ inches} \] and its radius \( r \) is: \[ r = \dfrac{130}{2} = 65\] The area of the tablecloth is equal to: \[ A = \pi r^2 = \pi \left( 65 \right)^2 \] \[ = 4225 \pi \approx 13,267 \text{ square inches} \]
Question 9
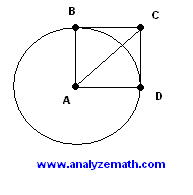
ABCD is a square with one vertex at the center of the circle and two vertices on the circle. What is the length of \( AC \) if the area of the circle is 100 square cm?
 .
.
\[ \text{Area of the circle} = \pi r^2 = 100 \] Solving for \( r^2 \): \[ r^2 = \dfrac{100}{\pi} \] Next, we use the Pythagorean theorem in triangle \( ABC \) to find the length of \( AC \): \[ AC^2 = AB^2 + BC^2 \] Since both \( AB \) and \( BC \) are equal to \( r \), we have: \[ AC^2 = r^2 + r^2 = 2r^2 \] Substituting the value of \( r^2 \): \[ AC^2 = 2 r^2 = 2 \left( \dfrac{100}{\pi} \right) = \dfrac{200}{\pi} \] Finally, taking the square root: \[ AC = \sqrt{\dfrac{200}{\pi}} = 10 \sqrt{\dfrac{2}{\pi}} \approx 8 \text{ cm} \]
Question 10
The ratio of the perimeter of circle \(A\) to the perimeter of circle \(B\) is 3:1. What is the ratio of the area of circle \(A\) to the area of circle \(B\)?
Let \(R_A\) be the radius of circle \(A\) and \(R_B\) be the radius of circle \(B\). The perimeters \(P_A \) and \( P_B \) of circles \( A \) and \( B\) are given by: \[ P_A = 2 \pi R_A \quad \text{and} \quad P_B = 2 \pi R_B \] The ratio of the perimeters of circle \(A\) to the perimeter of circle \(B\) gives: \[ \dfrac{P_A}{P_B} = \dfrac{2 \pi R_A}{ 2 \pi R_B} = \dfrac{3}{1} = \dfrac{R_A}{R_B} \] which simplifies to: \[ R_A = 3 R_B \] Now, we express the areas \(A_A\) and \(A_B\) of the two circles: \[ A_A = \pi R_A^2 = \pi (3 R_B)^2 \] \[ A_B = \pi R_B^2 \] The ratio of the areas is given by: \[ \dfrac{A_A}{A_B} = \dfrac{\pi (3 R_B)^2}{\pi R_B^2} \] \[ = \dfrac{\pi 9 R_B^2}{\pi R_B^2} \] \[ = 9 \] Thus, the ratio of the areas is \(9:1\).
Question 11
In a circle with center \( O \), a chord \( AB \) is perpendicular to the radius \( OP \), where \( P \) is the midpoint of the chord. If the length of the radius \( OP \) is 10 units and the distance from the center to the chord \( AB \) (i.e., \( OP \)) is 6 units, make a diagram for the problem and find the length of the chord \( AB \).
Let \( O \) be the center of the circle.
Let \( P \) be the point where the perpendicular from the center \( O \) meets the chord \( AB \), and let \( AB \) be the chord we need to find.
\( OP = 6 \) units (distance from center to chord).
By the Intersecting Chord Theorem, the perpendicular bisects the chord, so we have two right triangles: \( \triangle OAP \) and \( \triangle OBP \), both of which are congruent.
\( OA = OB = 10 \) units (radius of the circle).
Here is the diagarm for the problem.
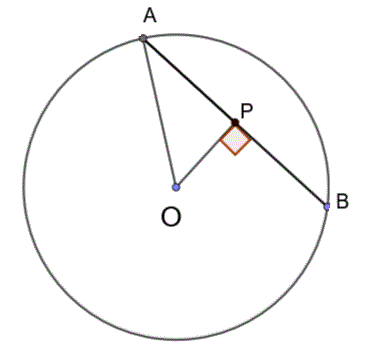
Using the Pythagorean Theorem in \( \triangle OAP \): \[ OA^2 = OP^2 + AP^2 \] Substituting the known values: \[ 10^2 = 6^2 + AP^2 \] \[ 100 = 36 + AP^2 \] \[ AP^2 = 100 - 36 = 64 \] \[ AP = \sqrt{64} = 8 \] Since \( P \) is the midpoint of \( AB \), the length of the entire chord \( AB \) is twice the length of \( AP \): \[ AB = 2 \times AP = 2 \times 8 = 16 \] The length of the chord \( AB \) is 16 units.