
Inverse function questions related to ordered pairs, linear, cubic root, square root, logarithmic and exponential functions are presented along with their detailed solutions. Answers are checked algebraically and graphically using the properties of a given function and its inverse. To be more effective, the questions need to be solved in order as each question makes it easier to understand the next.
Page Content
a) Find the inverse of function \( f \) given by: \[ f = \{( -2 , 0) , (0 , 1) , (2 , 3) , (3 , 4)\} \] b) Find the domain and range of the inverse of \( f \).
c) Let \( f^{-1} \) be the inverse of \( f \).
Evaluate: \[ f(f^{-1}(1)) \; , \; f^{-1}(f(0)) \; , \; f^{-1}(f(2)) \; , \; f(f^{-1}(3)) \] d) Graph \( f \) and \( f^{-1} \) on the same system of rectangular axes and write all properties of \( f \) and its inverse \( f^{-1} \).
The inverse of f is found by exchanging the input and output of the given function. Hence the inverse of f is given by \[ f^{-1} = \{(0 , -2) , (1 , 0) , (3 , 2) , (4 , 3)\} \] b)
Domain of \( f^{-1} \) : \( \{0 , 1 , 3 , 4\} \)
Range of \( f^{-1} \) : \( \{-2 , 0 , 2 , 3\} \)
c) \[ f(f^{-1}(1)) = f(0) = 1 \] \[ f^{-1}(f(0)) = f^{-1}(1) = 0 \] \[ f^{-1}(f(2)) = f^{-1}(3) = 2 \] \[ f(f^{-1}(3)) = f^{-1}(4) = 3 \] d)
The graph of \( f \) (blue) and \( f^{-1} \) (red) are shown below.

1) The graph of \( f \) and the graph of \( f^{-1} \) are reflections of each other line \( y = x \).
2) The x and y intercepts on the graph of \( f \) becomes y and x intercepts, respectively, on the graph of \( f^{-1} \)
3) The domain and range of \( f \) are the range and domain respectively of \( f^{-1} \)
4) \( f(^{-1}(x)) = x \) and \( f^{-1}(f(x)) = x \)
5) If function \( f \) is the inverse of function \( g \) then function \( g \) is the inverse of function \( f \) (a function and its inverse make a pair of functions)
Find the inverse of the linear function \( f(x) = 2x + 2 \) and graph \( f \) and its inverse in the same system of axes.
step 1: Replace \( f(x) \) by \( y \) and rewrite the function as an equation as follows \[ y = 2 x + 2 \] step 2: interchange \( x \) and \( y \) in the above equation \[ x = 2 y + 2 \] step 3: Solve the above equation for \( y \) \[ 2 y = x - 2 \] \[ y = (1/2) x - 1 \] Step 4: Write the inverse using the inverse function notation \[ f^{-1} (x) = (1/2) x - 1 \] Step 5: Check the answer obtained using the properties : \( f(^{-1}(x)) = x \) and \( f^{-1}(f(x)) = x \)
One way to check the answer obtained is to make sure that \( f(^{-1}(x)) = x \) and \( f^{-1}(f(x)) = x \).
\[ f(f^{-1}(x)) = 2(f^{-1}(x)) + 2 = x - 2 + 2 = x \]
\[ f^{-1}(f(x)) = (1/2) f(x) - 1 = (1/2)(2 x + 2) - 1 = x + 1 - 1 = x \]
The graphs of \( f \) and \( f^{-1} \) are shown below and we can easily see that the graphs are reflection of each other on the line \( y = x \). This is a graphical method to check whether a pair of functions are inverse of each other.
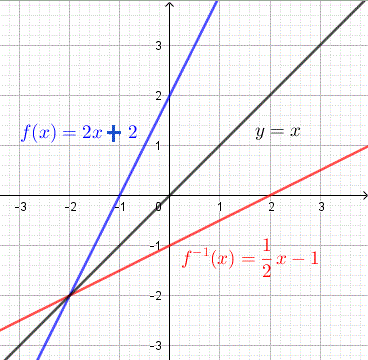
Find the inverse of the function \( g(x) = \sqrt[3] {x - 1} \) and graph \( g \) and its inverse in the same system of axes.
Raise both sides of the equation to the power 3 and simplify
\[ x^3 = (\sqrt[3] {y - 1})^3 \]
Simplify
\[ x^3 = y - 1 \]
Solve for \( y \)
\[y = x^3 + 1 \]
Step 4: Use the inverse function notation to write
\[ g^{-1} (x) = x^3 + 1 \]
Step 5: Check algebraically the answer using the properties : \( g(^{-1}(x)) = x \) and \( g^{-1}(g(x)) = x \)
\[ g(g^{-1}(x)) = \sqrt[3] {g^{-1}(x) - 1} = \sqrt[3]{x^3 + 1 - 1} = \sqrt[3]{x^3} = x \]
\[ g^{-1}(g(x)) = g(x)^3 + 1 = (\sqrt[3]{x - 1)})^3 + 1 = x - 1 + 1 = x \]
We can easily check that the graphs of functions \( g \) and \( g^{-1} \) , shown below, are reflection of each other on the line \( y = x \) and are therefore inverse of each other.

Find the inverse of the function \( h(x) = \ln(x - 1) \) and graph \( h \) and its inverse in the same system of axes.

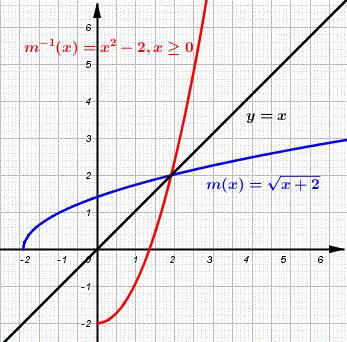
Find the inverse of the function \( m(x) = \sqrt{x + 2} \)
Step 4: Use inverse function notation
\[ m^{-1} (x) = x^2 - 2 \; , \; x \ge 0 ; \text {(restricted domain)} \]
Step 5: Check algebraically the answer
\[ m(m^{-1}(x)) = \sqrt{m^{-1}(x) + 2} = \sqrt{x^2 - 2 + 2} = \sqrt{x^2} = | x | = x \; \text{because} \; x \ge 0 \]
\[ m^{-1}(m(x)) = (m(x))^2 - 2 = (\sqrt{x + 2})^2 - 2 = x + 2 - 2 = x \]
The graphs of \( m \) and \(m^{-1} \) shown below are reflection of each other on the line \( y = x \) and are therefore inverse of each other.
Find the inverse of the function \( t(x) = \dfrac{1}{x-1} \)
